
1989 R
DIGICAM (Digital Camera) - 1989. The
first use of the word digicam that we have found was as a trademark
name owned by J & G Coughtrie Ltd Montrose Avenue, Hillington,
Glasgow, G52 4LZ, United Kingdom, dated 6 January 1989 (trade mark
number UK00001369395), but it is no longer in effect.
https://www.ipo.gov.uk/tmcase/Results/1/UK00001369395
http://www.yourdictionary.com/digicam
http://www.wordsense.eu/digicam/


https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/cameras/item/fujix-ds-x
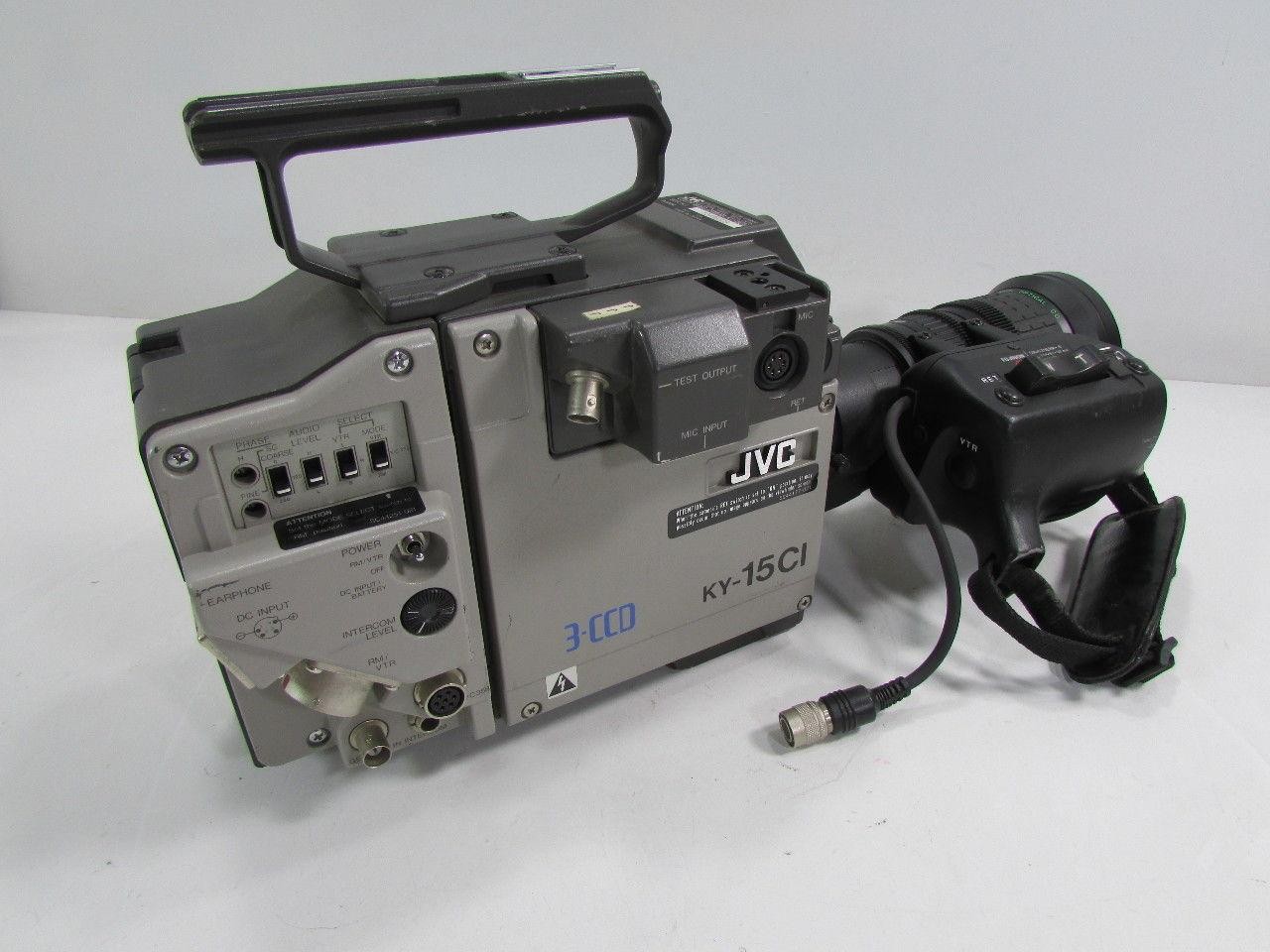



JVC KY-15CI- 1989. The
KY-15CI was a high-resolution, three-CCD color camera for image capture
in computer-graphics applications. The KY-15CI was designed for direct
connection to TARGA, VISTA, and Raster Ops image capture boards through
a 9-pin connector supplied with the camera. The KY-15CI had a
resolution of 668 X 485 pixels and used a one-line scanning technique
that produced a significant increase in vertical resolution. An optical
prism was used to separate the red, green, and blue primary colors for
color reproduction. The camera's electronic shutter stopped action down
to 1/500 second per field. MSRP $6,395. The above ad is from the October 1989
issue of Computer Graphics Review. Strangely, even though that
magazine had ads in 1989 for the Canon RC-470 and JVC KY-15CI cameras
which could be used as input devices for computer graphics, they
had no review or mention of such cameras, only scanners and digital
frame grabbers as input devices.
http://pro.jvc.com/prof/attributes/tech_desc.jsp?model_id=MDL100821&feature_id=02
http://pro.jvc.com/prof/attributes/features.jsp?model_id=MDL100821&feature_id=01
http://pro.jvc.com/prof/attributes/press_res.jsp?model_id=MDL100821&feature_id=08
KODAK ECAM / D-5000- 1989. In 1989, Steve Sasson and a colleague, Robert Hills, created the first modern digital single-lens reflex (S.L.R.) camera that looks and functions like today's professional models. It had a 1.2 megapixel sensor, and used image compression and memory cards. But Kodak's marketing department was not interested in it. Mr. Sasson was told they could sell the camera, but wouldn't because it would eat away at the company's film sales. The 1989 version of the digital camera, known as the Ecam (electronic camera) was the basis for a United States patent issued on May 14, 1991. Until it expired in the United States in 2007 the digital camera patent helped earn billions for Kodak, since it was not Mr. Sasson who owned it, making most digital camera manufacturers pay Kodak for the use of the technology. Though Kodak did eventually market both professional and consumer cameras, it did not fully embrace digital photography until it was too late. In 2012 Eastman Kodak filed for bankruptcy. NOT MARKETED.
A previously unknown close connection between Chinon and the Kodak ECam is discussed by Ralf Jannke at: https://www.digicammuseum.de/gechichten/erfahrungsberichte/logi-fotoman-pixtura-iichinon/
As Ralph points out, Chinon
has had a lot more to do with the development of digital photography
than most people are aware of, including the 1989 Kodak ECam.
"Not only does this Kodak camera feature a Chinon lens, the red-marked
LCD display on top of the 1987 analog Chinon CP-7m with a Pentax K
mount and the digital Kodak prototype E(electronic)Cam(era) are likely
identical."
http://lens.blogs.nytimes.com/2015/08/12/kodaks-first-digital-moment/?_r=0
http://www.google.com/patents/US4131919
https://www.google.us/patents/EP0289944A1?cl=zh
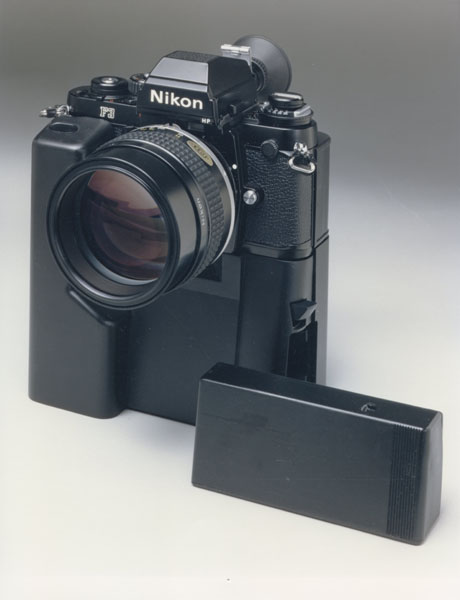
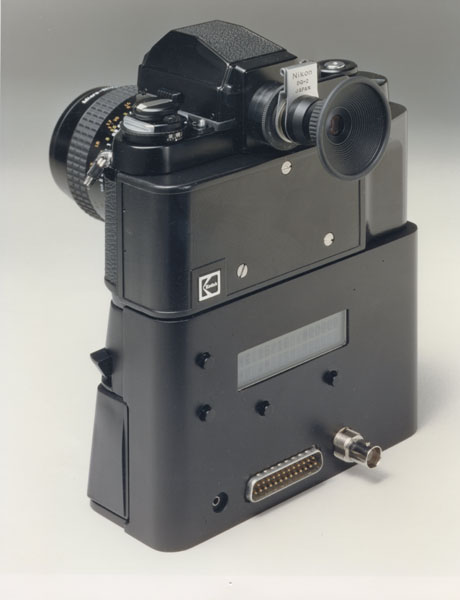


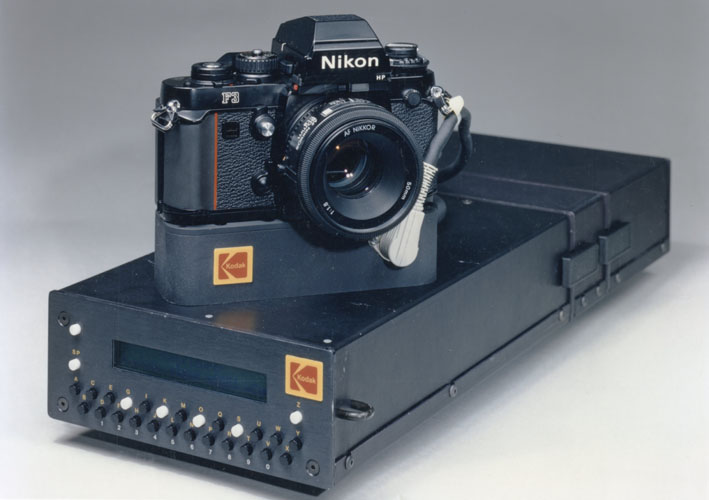
KODAK HAWKEYE II INTEGRATED IMAGING ACCESSORY DIGITAL CAMERA - 1989. This
camera was a follow-up of the 1988 Kodak digital Tactical Camera which
was tethered to a shoulder pack. The Hawkeye II integrated camera
replaced the shoulder pack with a housing attached to a Nikon F3 body
and thus was more suitable for demonstrating this new digital
technology. Images were stored in DRAM on an Image Storage Module that
plugged into the side of the camera. Images were either four of 1280 x
1024 pixels or sixteen of 640 x 512 pixels. It
was designed by Kodak's James McGarvey, lead engineer in Kodak's
Federal Systems Division who kindly supplied the above photo and
information. Renae Sanger did the mechanical design drawings. Bruce
Crosman and Joanne Schieyer designed the circuit boards which were hand
assembled by Tom McCarthy. NOT MARKETED.
Much more information concerning this and
other early Kodak DSLRs can be seen on Mr. McGarvey's web site at http://jemcgarvey.com

KODAK HAWKEYE II TETHERED IMAGING ACCESSORY DIGITAL CAMERA - 1989. This was a tethered version of the above camera. NOT MARKETED.
KONICA
KANPAI - 1989. Konica's Kanpai was
the
world's first voice activated camera and would automatically swivel on
its built-in tripod to take snapshots wherever it heard a burst of
sound
like laughter or cheers. The original 1989 model was red, later models were black. "Products to Watch," Fortune. Mar.
25, 1991.
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Konica_Kanpai

 MACINTOSH PROFESSIONAL
IMAGE PROGRAM - 1989. Letraset released Color
Studio 1.0, the first professional image manipulation program for Macintosh
computers.
MACINTOSH PROFESSIONAL
IMAGE PROGRAM - 1989. Letraset released Color
Studio 1.0, the first professional image manipulation program for Macintosh
computers.
http://www.fotomuseum.ws/archive/photo/timeline/decade/1975.htm
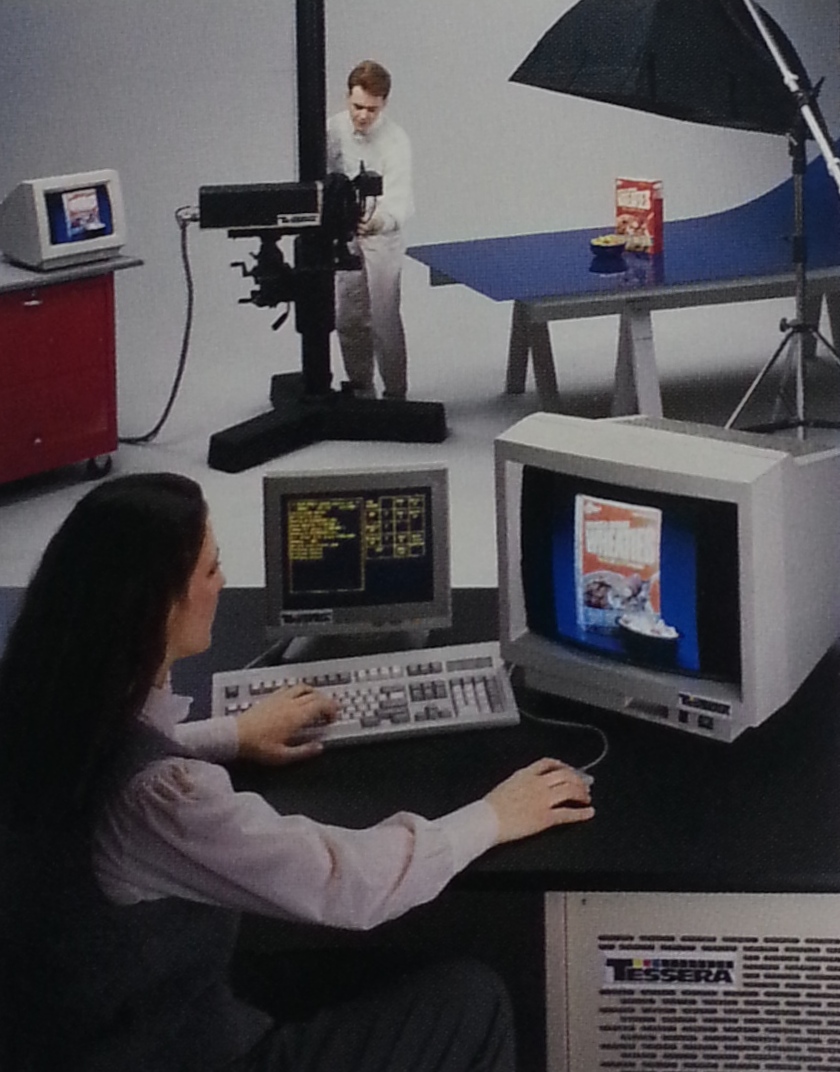
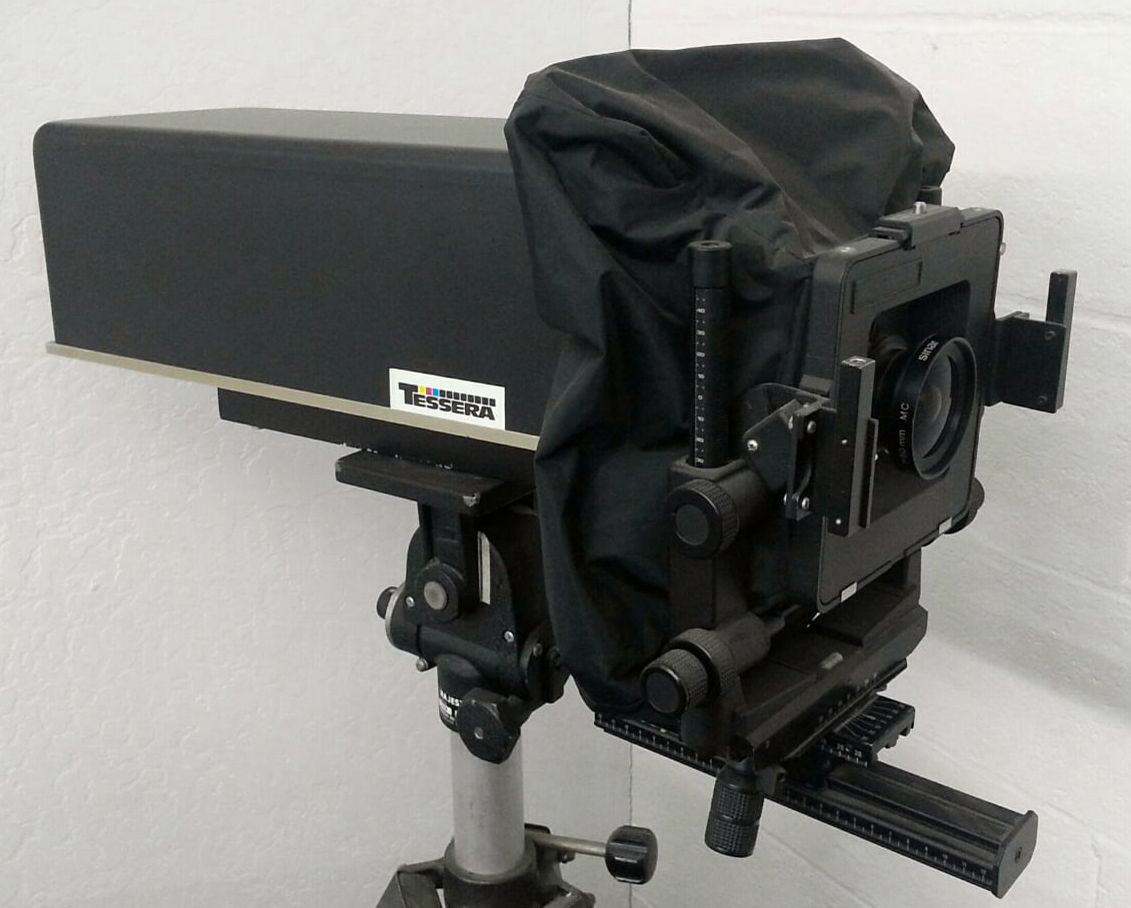



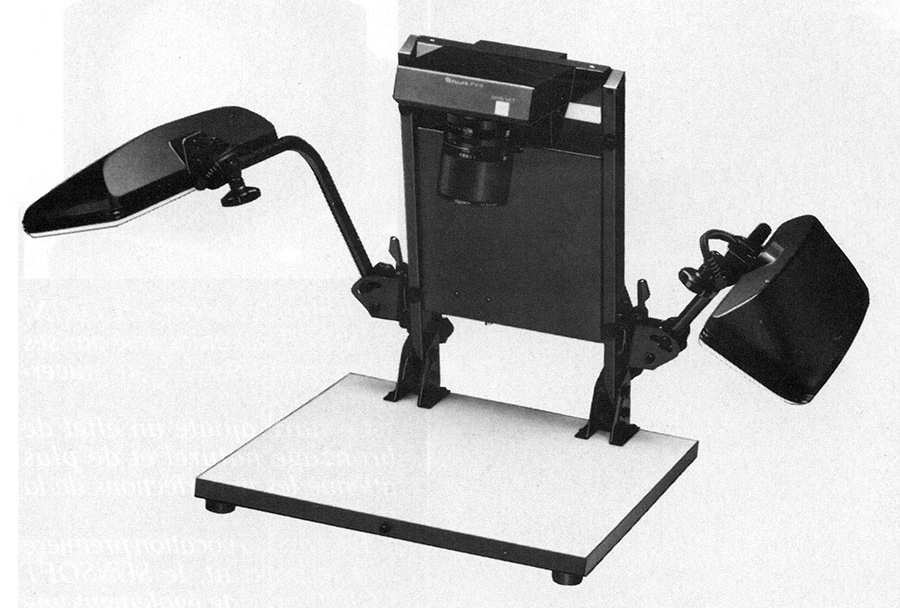
MEGAVISION TESSERA - 1989. The
first Tessera system went into regular use in early 1989 at a
commercial photo studio in Minneapolis (Photo Mechanical Services,
Inc.). Shooting 4 Megapixel images in a production photo studio,
believed to be the world's first professional digital camera
system. Many thanks to John Cox of Megavision for providing these
very rare photos to DigiCamHistory.Com.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MegaVision_%28cameras%29
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/cameras/item/megavision-tessera


![]()
NINTENDO GAME BOY - 1989. Model DMG-01, the first Game Boy, was released in 1989.
http://www.gizwizsearch.com/episode-595.html
https://www.google.us/patents/EP0289944A1?cl=zh
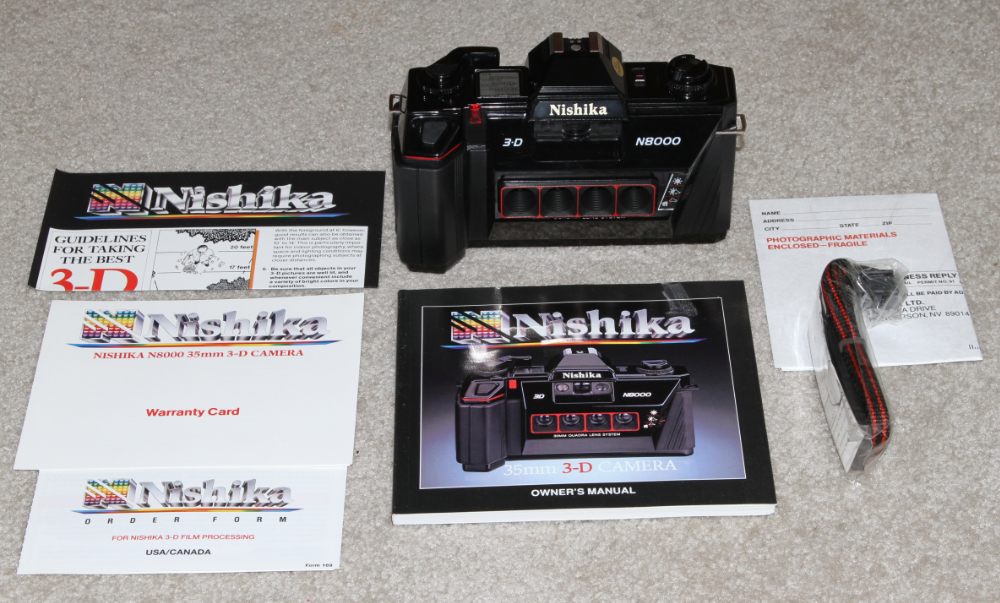


![]()
NISHIKA N8000 - 1989. Nimslo, a manufacture of inexpensive 3D cameras, went bankrupt and was partly sold to a Nevada company called Nishika . In April 1989, Nishika introduced the four lens Nishika N8000 and later the four lens N9000. The N8000 featured a plastic body with plastic lenses, a fixed 1/60 shutter speed and a 3 position manual aperture lever that that selected f8, f11 and f19.
http://wikipedia.org/wiki/Nimslo

PCMCIA - 1989. Personal Computer Memory Card International Association,
an international standards body founded to establish standards for
Integrated circuit cards and to promote interchangeability among mobile
computers.
http://www.thinkwiki.org/wiki/PCMCIA

SANYO STILLVISION SVC-05 - 1989. Prototype electronic still camera. 390K CCD. Programmed auto-exposure, auto-flash, auto white balance, Shutter speed up to 1/2500 second. MSRP $800. Popular Photography, March 1989, p53. NOT MARKETED.
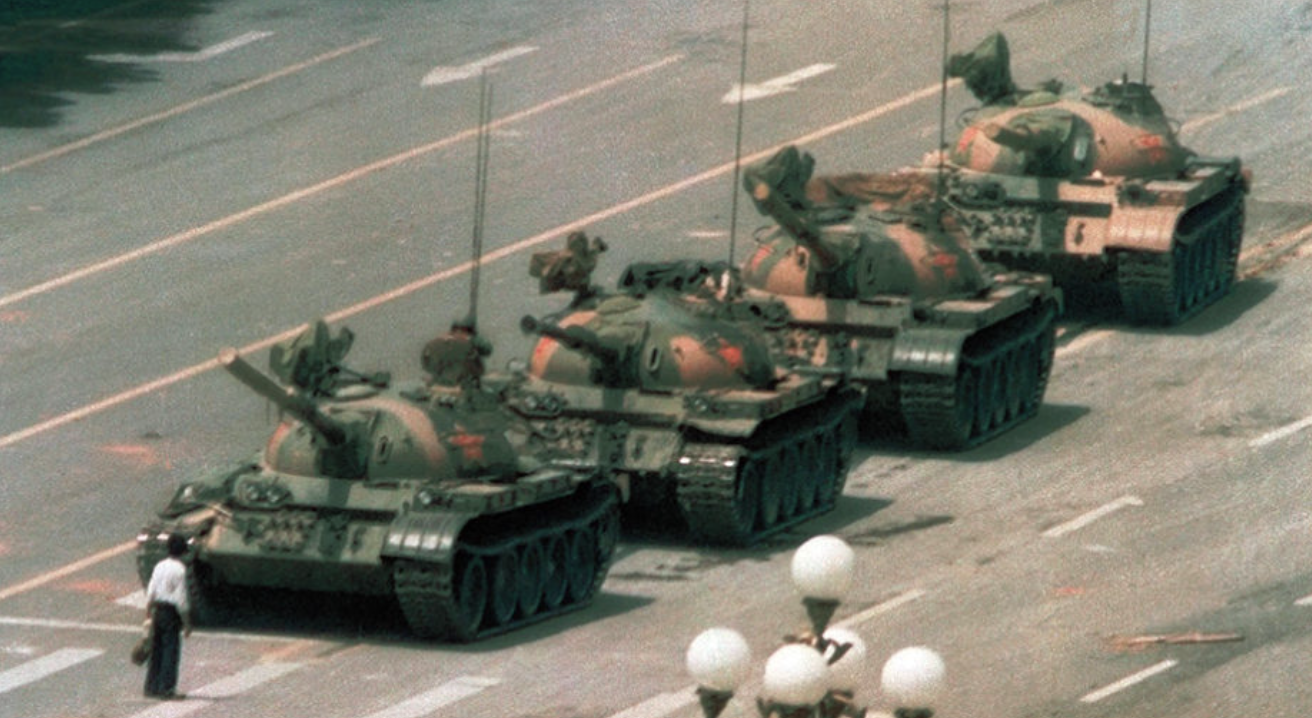

SONY DIH 2000 DIGITAL IMAGE HANDLER - 1989. The DIH2000 could capture single frame images from any video source, motion or still video cameras, and transmit them over standard phone lines in as little as ten seconds. Sony won a special Emmy Award, Still-Picture Transmission Technology for News, honoring Sony for its development of still-picture transmission capabilities, particularly as it related to the 1989 student uprising in Tiananmen Square, China. During the demonstrations the Chinese government blocked the transmission of live video. News networks were forced to send their video tapes to Hong Kong for transmission thereby delaying their broadcasts by more than twelve hours. CCN sent a crew into the field using a Sony Mavica still-video recording system (Mavica MVC-5000 camera) and sent their images over the Chinese telephone system to CNN's U.S. studios. CNN delivered images to its audience many hours ahead of the competition. Effects of those still images on American and European audiences was electrifying. The Day The Image Stood Still, Paul Saffo, Personal Computing, February 1990, p59. Digital Photography: Pictures of Tomorrow, John Larish, 1992, p4, p141. We believe we were the first digital camera history web site to provide a photo and information concerning this item.



![]()

The
DIH 2000 and Sony still video camera (ProMavica MVC-5000) were also
used
during the Persian Gulf War by the U.S. Army to transmit photos to the
Army Media Services Branch in Washington, D.C.



![]()
SONY ProMavica
MVC-5000 - 1989. The Sony ProMavica MVC-5000
(MAVICA = Magnetic Video
Camera)
still-video camera. The MVC-5000 was the first to transmit almost
instantaneous still color images over phone lines using Sony DIH2000
noted above and was the camera used by the CNN crew in China to
transmit the Tienemen Square images. The ProMavica recorded images as
magnetic impulses on a compact 2-inch still-video floppy disk.
The images were captured on the disk by using two CCD (charge-coupled
device) chips. One chip stored luminance information, and the
other separately recorded the chrominance information. This
camera provided a 720,000-pixel image. The images could be stored on
the floppy disk either in Frame or Field mode. When Frame was
selected, each picture was recorded on two tracks and up to 25 images
could be recorded on each disk. When Field was selected, each
picture was recorded on only one track, allowing up to 50 images to be
recorded. When recorded in the Field mode, images were less
detailed as compared to images recorded in the two-track Frame
mode. The MVC-5000 was considered to be the leader in image
quality during its time. The MVC-5000 recorded still video
hi-band resolution at 500 TV lines versus the standard 360 lines of
most other still video cameras of that period. Images could be shown on
a TV by using the Sony MVR-5500A shown below. MSRP
$10,000. Electronic Still Video, Folio, 1 February
1991, p75. Digital Photography,
Mikkel Aaland, 1992, p17. (Rare on U.S. eBay)
http://www.nikonweb.com/mvc5000/
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/esvc/item/sony-promavica-mvc-5000

![]()
Sony MVR-5500A
https://www.bly.com/newsite/Pages/PDFs/companynews-sony.pdf
https://pixinfo.com/cikkek/tortenelem-sony/#google_vignette



![]()
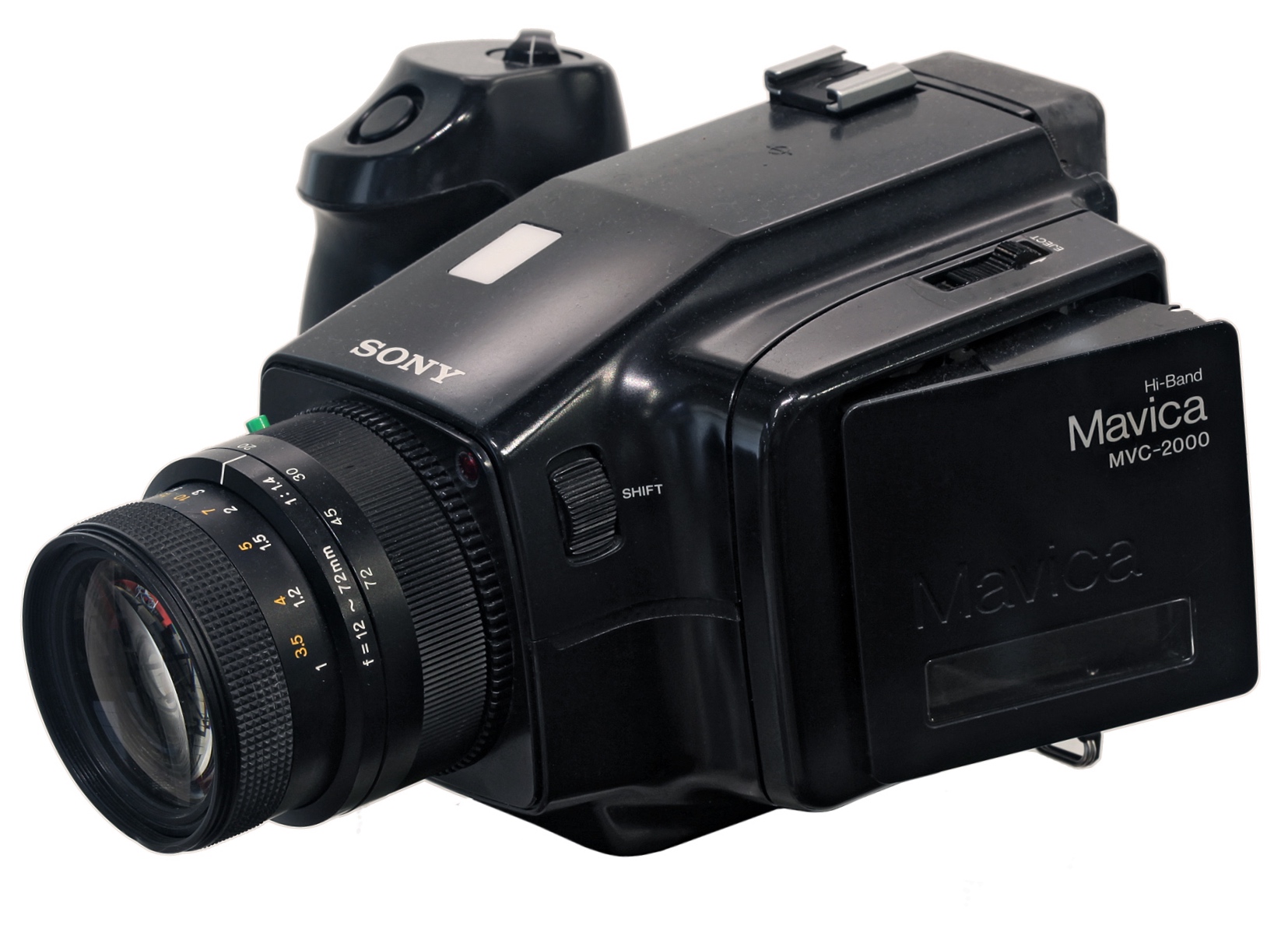
SONY ProMavica
MVC-2000/PF - 1989.
The MVC-2000PF was a pre-production, hand-built camera sent to specific
photographers for testing (see our 1986 page). The production
model went on sale in
1989. This analog still video camera had a 13X zoom lens and was
available only in NTSC. It was a one-CCD camera of 2/3-inch and
380K pixels. 48mm to 288mm f/1.4 zoom lens. Shutter 1/15 to
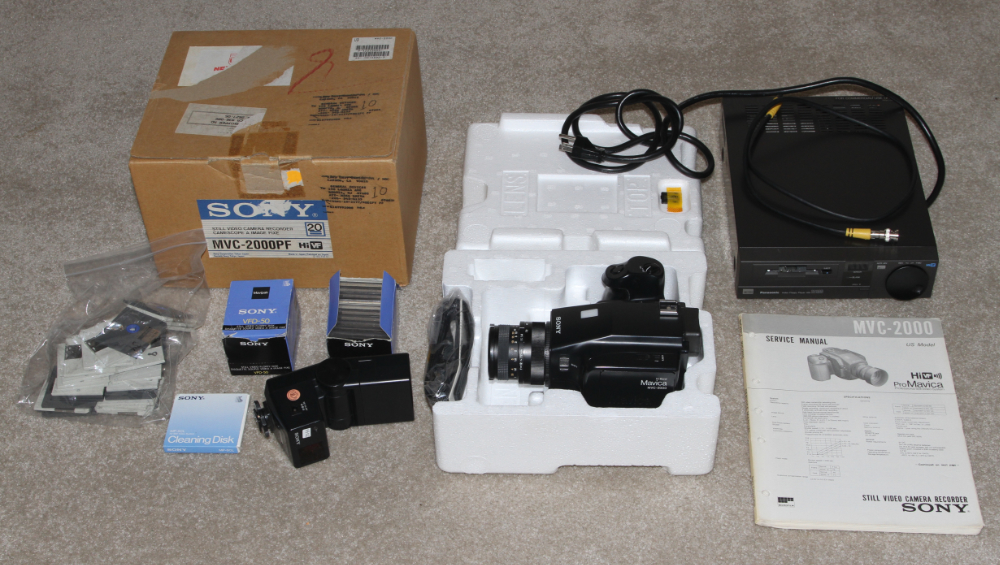
1/1000. The upper right photo shows the MVC-2000PF new in the box
along with the Sony MFL-30 flash made for that camera, the service
manual which also included the operation instructions, several boxes
of new mini floppies, a mini floppy disk cleaner, several dozen used mini
floppies, the original MVC-2000PF carton, and a Panasonic AG-ES100 mini floppy disk player. MSRP in 1989 for the MVC-2000 was $3,395.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sony_Mavica
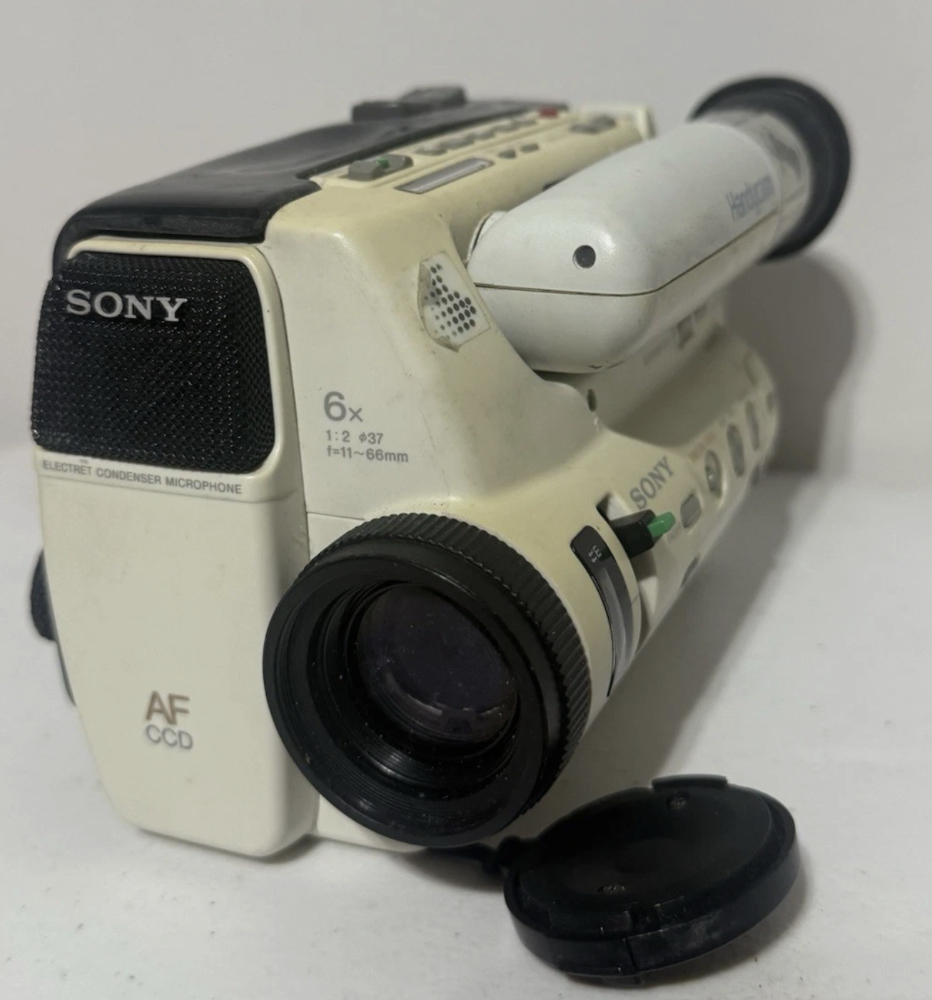
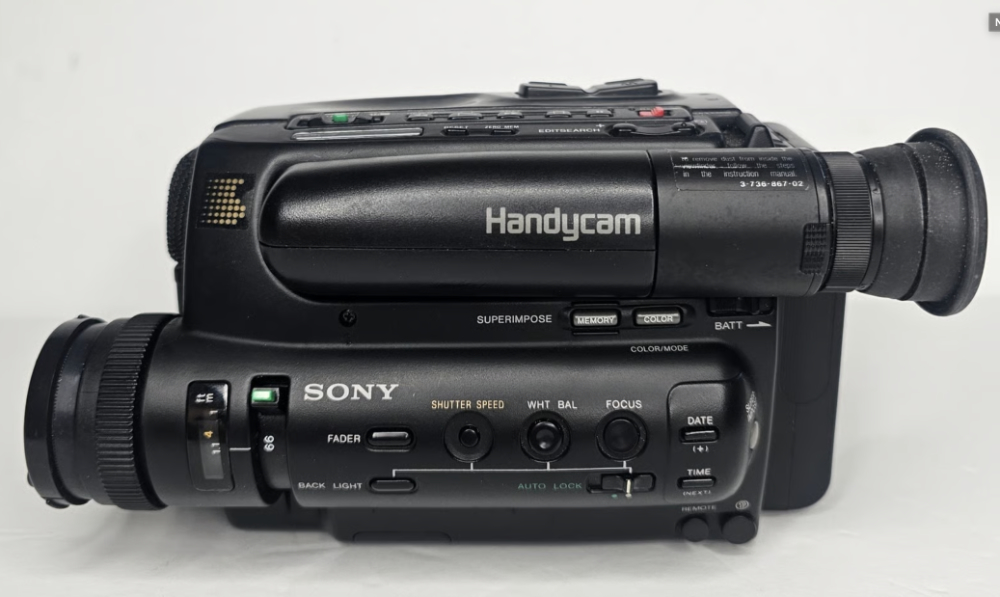



![]()
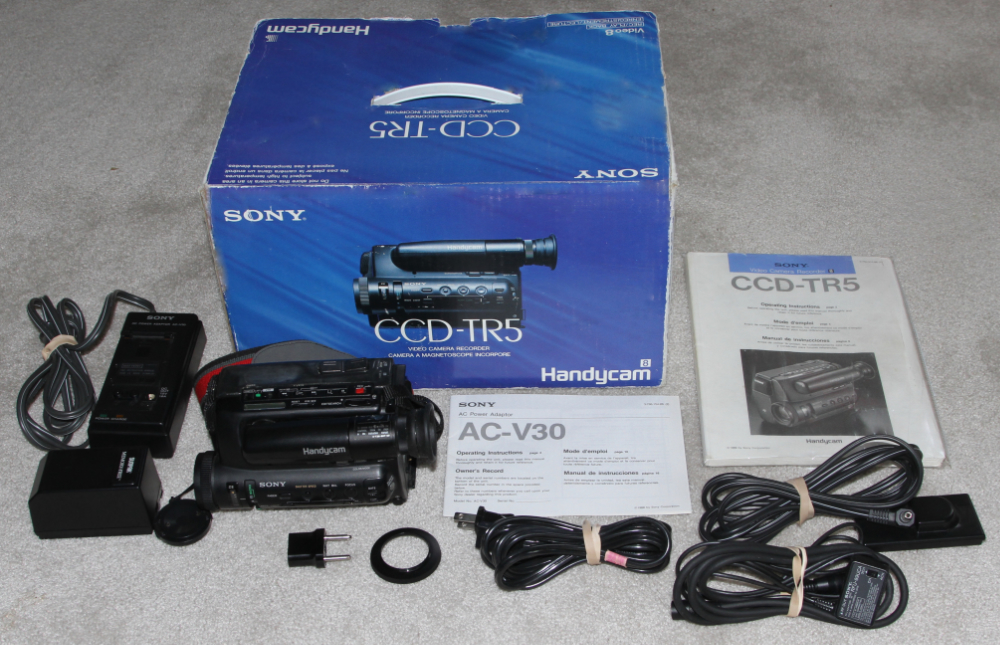

ttps://www.sony.com/en/SonyInfo/design/gallery/CCD-TR55/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W1bM2KoKjyc
FOR MORE INFO CLICK HERE


See
video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pwtJ5wU1Izg&t=261s
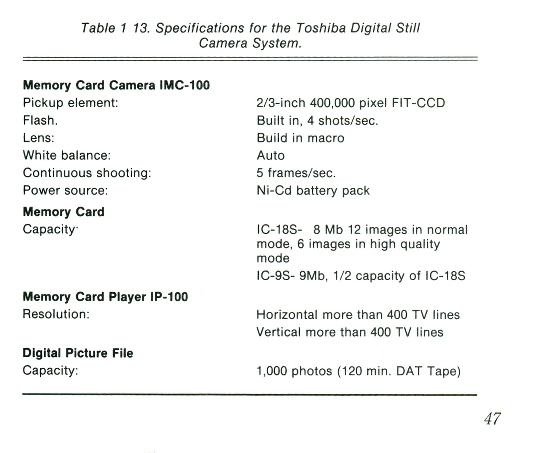

TOSHIBA
IMC-100 - 1989.
Similar to the Fuji DS-X above (cameras were supposedly jointly
developed by Toshiba and Fuji). 2/3-inch 400K pixel
CCD, and along with the DS-X, first consumer / professional handheld
digital camera sold to the public and which stored digital images on a
flash card. Images were captured on a credit-card-sized removable memory card. Auto white balance,
built-in flash, built-in
macro, 5 images per second burst. Used IC-18s-18MB memory card
with
six-image capacity in high resolution mode. Continous shooting up
to five frames per second. Understanding Electronic
Photography,
John J. Larish, 1990, p47. A
Toshiba press release at the time contained a drawing of what Tosiba
described as "The Applications of the Toshiba Digital Card Camera
System". At the center of the drawing was the camera shown
above. Marketed in Japan only. MSRP $3,999 ($10,000 in 2024 dollars)
http://dchis.com/Fuji%20DS-X.html

https://www.quora.com/What-was-the-first-commercial-digital-camera-available-to-the-public-and-who-created-
http://toshiba-mirai-kagakukan.jp/en/index.htm


TOSHIBA IC-100 - 1989. Images were captured on a credit-card-sized removable memory card. The card held up to thirteen images and could be transferred to Toshiba's digital audio tape (DAT) recorder. Up to to 1,600 photos could be stored on one 120-minute DAT cassette tape. Popular Science, December 1989, page 53. NOT MARKETED.
See Popular Science, December 1989, page 53.
https://books.google.com/books?id=dwEAAAAAMBAJ&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/prototypes-rarities/item/toshiba-ic100
https://www.0youtube.com/watch?v=BPxm-bJGtuI Toshiba SK-3D7 VHS-C VIDEO .
https://forum.videohelp.com/threads/401404-Converting-vhs-c-tapes-with-3d-field-sequential-video-from-Toshiba-3d-cam FVideoHelp Forum.

Vivitar V-2000 description in 'Understanding Electronic Photograph' by John Larish
VIVITAR V-2000
- 1989. Still video camera
prototype called the V-2000.
Images recorded to floppy disk. 360K CCD. Selectable 9mm
f/2
or 16mm f/2.5 lens. Auto-white balance and built-in flash. Understanding
Electronic Photography,
John J. Larish, 1990, p20 and p42. (Photo not
available). NOT MARKETED.
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/prototypes-rarities/item/vivitar-v-2000
1989