

1980 - 1983 R


FIRST CCD COLOR VIDEOCAM, SONY XC-1 - 1980. In 1980, Sony marketed a commercial color videocam using a CCD. The world's first commercial color video camera to utilize a completely solid state image sensor, a charge-coupled-device, or CCD. It was also the smallest camera on the market, weighing only 2.8 pounds.

![]()
MAMIYA ZE 35 - 1980. The ZE 35 was among the last of the 35mm SLR cameras produced by Mamiya. It was the first Japanese SLR to use an electronic coupling system to transmit information between the camera body and its interchangeable lenses. List $365 (about $1020 in 2012 dollars). Many 35mm SLRs such as the one above are readlly available on eBay in near mint condtion and at very low prices. Such cameras can be be jewels of any camera collection.
http://herron.50megs.com/ZE.htm

![]()
RICOH A-100 - 1980. The Ricoh A-100 was an automatic, 35mm, SLR camera launched by Ricoh in 1980. The A-100 featured aperture priority AE mode and electronically-controlled focal plane shutter. The camera was equipped with multi-coated XR Rikenon 50mm f/1.4 standard lens made of 7 elements arranged in 6 groups, but it could also use other Rikenon K mount interchangeable lenses. The A-100 was powered by two 1.5V silver oxide batteries (JIS G13, Mallory MS76, or Eveready S76).
http://www.brennanprobst.com/2012/12/spotlight-ricoh-100-super.html


IBM
PC 5150 - 1981. The IBM PC ( PC =
Personal
Computer ) model #5150, was conceived by a team of IBM engineers in
Boca
Raton, Florida in early 1980. The IBM PC was introduced on August
12, 1981. Digital Photography, Mikkel Aaland, 1992, p11.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IBM_Personal_Computer

3.5-INCH FLOPPY DISK - 1981. Sony introduces the floppy that we are all familiar with today - 3.5 inches or 90mm. A variety of disks of various sizes had been produced to take the place of the 5.25-inch disk, but when several companies adopted Sony's 3.5-inch format it became the industry standard.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floppy_disk

![]()
FUJICA AX-1- 1981. Shutter
1/2 - 1/1000 sec. Lens Fujinon f/3.5-4.5, 43-75 mm zoom. The lens and
camera in excellent condition were obtained on eBay with a winning bid
of $9.95.
http://www.pentax-manuals.com/fujica/cameras/ax1.htm


![]()
PENTAX ME-F
- 1981. World's first SLR (single lens reflex)
camera with TTL (through-the-lens) autofocus capability. Click on image
to see enlarged view.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pentax_ME_F

![]()
POLAROID THE BUTTON - 1981 . Donated by Tatiya Hwang. One of several Polaroid cameras that used the
same film packs as the much more expensive Polaroid SX-70 camera.
http://en.polaroid-passion.com/format-SX-70-cameras.php?id=68
POLAROID
8x10 81-12 FILM PROCESSOR - 1980. Polaroid began producing film in wide varieties,
including 8x10 instant transparencies (Type 891) and instant
orthochromatic, translucent prints (Type TPX). To process these
products Polaroid marketed a series of film processors which allowed
processing their 8x10 products without a darkroom or chemical
solutions. Above are shown a model 81-12 film processor and 81-09
loading tray. These items are still common on eBay, but the film
products may be expensive and out-of-date.
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Polaroid_instant_film
https://adage.com/article/adage-encyclopedia/polaroid/98826
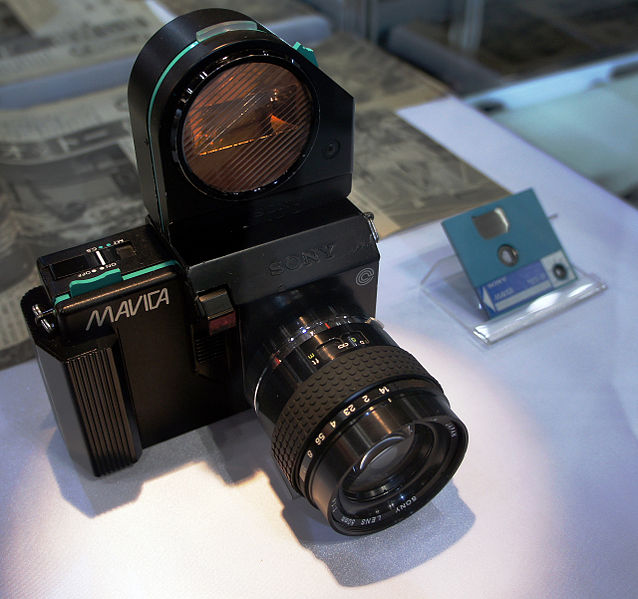



SONY
MAVICA ELECTRONIC CAMERA - 1981. A
new
era In photography begins. On August 25, 1981, at a packed
conference in Tokyo, Sony unveiled a prototype of the company's first
still
video camera, the Mavica (Magnetic
Video
Camera). It recorded images on
two-inch
floppy disks and played them back on a TV set or Video monitor.
The
Mavica was not a digital camera, but a TV camera capable of writing TV
quality stills onto magnetic disks, with a shutter that would allow it
to freeze frames within the limits set by twin-field interlace making
up
the complete frame. The Mavica was a single lens reflex with
interchangeable
lenses. The original Mavica was provided with three
bayonet-mounted
lenses: a 25mm f/2, a 50mm f/1.4, and 16-65mm f/1.4 zoom. CCD
size
was 570 x 490 pixels on a 10mm x 12mm chip. F/stop was controlled
manually according to lighted arrows that appeared in the
viewfinder.
Light sensitivity was rated at ISO 200. The original Mavica had
only
one shutter speed, 1/60th second. Each image was recorded in its
own single circle on the floppy disk that Sony called the Mavipak.
Up to fifty color photos could be stored on one Mavipak. Multiple
exposure of 2, 4, 8. or 20 images could be selected. The Mavica
was
powered by three AA-size batteries. Images were displayed on a
television
set and were considered to be equal in quality to the maximum
capability
of a TV set of that time. NOT MARKETED.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3t7svq2kXGI
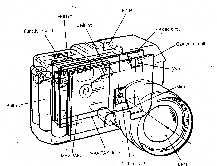
Cutaway
Drawing of the Sony Mavica
First
Operational Electronic Still Camera
Click
on image to see full-page view.
Sony
Advertisement Announcing the Sony Mavica Electronic Still Video Camera
________________________________________________________________________________
Announcement SONY CORPORATION
Sony Corporation today announced that it has developed a revolutionary video still camera, embodying fully the advantages of advanced electronic technology in magnetic recording, CCD and IC semiconductors.
Called the MAVICA system, the new magnetic video still camera uses no photographic film and therefore does not require developing and printing processes which are indispensable to conventional chemical photography. This new video still camera represents an epoch-making innovation in the history of still photography.
The conventional camera has seen some improvements over the years, such as the change from dry plate to film, the use of electronics in certain parts, and the reduction of size and weight. However, for more than 140 years since the invention by Daguerre of France, there has been no fundamental change in the concept and technology of photography, in which images are recorded on film through chemical reactions of photo-sensitive materials.
Sony's MAVICA system replaces each chemical processes with an electromagnetic system. The MAVICA is no larger than a conventional 35mm single-lens reflex camera. An image that comes through the lens is converted into electronic signals by a solid-state imager called CCD (Charge Coupled Device), previously developed by Sony. The signals are recorded on a very small magnetic disk called MAVIPAK that Sony has developed for the new camera system.
The newly developed memory medium called MAVIPAK can record 50 still color pictures. The recorded pictures can be viewed immediately on the home TV set through a specially designed playback unit called the MAVIPAK Viewer. MAVIPAK pictures require no developing or printing processes such as required in chemical photography. It is expected that hard copies of color pictures can be produced from the MAVIPAK by means of a new color printer now under development by Sony.
____________________________________________________________________________


FLOPPY
DISK DRIVE - 1981. Sony introduces
the
first 3.5 inch floppy disk drive.
https://www.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sony_Mavica





The article on the right was posted by the Fairchild ASI
Science Team on the University of Calgary physics web site
. Downloaded 8/28/2002
Photos on the above left and the below aurora image were included in the same article.
UNIVERSITY
OF CALGARY FAIRCHILD ALL-SKY CCD CAMERA -
1981. In 1981, the University of Calgary Canada
ASI (All-Sky Imager) Science Team constructed the first operational digital
camera which used a CCD (previous digital versions of the Calgary All-Sky Camera used an imager tube).
The All-Sky camera used the first commercially available CCD, the
Fairchild
100 x 100 pixel CCD of 1973 (see 1970s page), thus the name, Fairchild
All-Sky Camera. Unlike other early electronic cameras, the
All-Sky
Camera provided digital data rather than analog data, thus making it
the
first documented operational digital camera using a CCD imager. It was used to photograph
auroras.
Shown above left to right: camera exterior, camera interior, camera on
location. Shown below: Image of an aurora captured by
the UC Fairchild All-Sky Camera. NOT MARKETED.
http://aurora.phys.ucalgary.ca/index_past.html
https://www.cnet.com/news/photos-the-history-of-the-digital-camera/
=onepage&q=UNIVERSITY%20OF%20CALGARY%20FAIRCHILD%20ALL-SKY%20CCD%20CAMERA%20-%201981&f=false



![]()
HITACHI VK-C1000
- 1981. First consumer video camera
with solid state (MOS - metal oxide semiconductor, 384 x 485 pixels) image pickup device rather
than an image pickup tube. The viewfinder was a small color CRT rather
than an LCD. The recording device was basically a table-top VTR with a
shoulder strap attached. The battery was very large and was usable for
about 45 minutes of recording. A separate power supply was required to
operate the VTR when not on battery power. Compare with today's palm-sized camcorders.
EIKONIX- 1982.
Eikonix Corporation marketed the first digital filming
instrument. It had a 3000 pixel scanner which moved across 4000
lines to provide a 12MP image. First images were shades of grey,
but later red, blue and green filters were added resulting in the first
digital color film. It was generally utilized in scientific
laboratories. Industrial Light and Magic, an American special cinema
effects company, founded by the creator of “Star Wars”, George Lucas,
used it to digitalise, frame by frame, his first films.
https://www.cameramuseum.ch/en/discover/permanent-exhibition/the-digital-revolution/eikonix-and-the-beginning-of-digital-camera-work/




![]()
SONY
CDP-101 - 1982. The CD player prototype Goronta was shown at the Audio Fair in the Fall of 1981 (photo on the left). On 1 October
1982 the Sony CDP-101 was released
- the world's first consumer compact disc player. The Compact
Disc was digital, reconstructing sound from a rapid stream of 1's and
0's stored sequentially on the disc. Sony chose 101 as the model number
to represent the digital 1's and 0's. Although
pundits of the time predicted that it would be at least ten years before CDs made
serious
inroads into LP sales, and that CD players would never be made for
automobiles
because they "weren't needed," CDs quickly took over the
recorded
music market and relegated LPs to the realm of collectors and vinyl
diehards. MSRP: $900.
http://www.cedmagic.com/history/sony-cdp-101.html
SCANNER IMAGE TRANSMISSION - 1982. Kodak demonstrated image transmission using a scanner. Don Sutherland, "Digital Deal," Photo trade News, Chapter 3, August 2000.
Nikon FM2 - 1982-2001. Sometimes you have you pay more than $10-20 to win and item on eBay, but that's OK if you get more in quality or value. The above purchase is an example of both. The Nikon FM2 had an original price of $364 for the body only. That would be about $873 in 2010 dollars. By 1995 the MSRP had risen to $745 ($1065 in 2010 dollars). The above FM2 along with three lenses, two flash units, a Weston III light meter, three filters, a self timer, a remote, a lens hood, and four lens containers, all in excellent condition, were purchased on eBay for $102.50. The unheard of 1/4000 sec shutter speed was unique to the FM2 at the time of its introduction.
http://www.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nikon_FM2


![]()
![]()



DISC CAMERAS - 1982. Kodak began marketing disc photography in 1982 with a line of compact cameras built around a rotating disc of film. A variety of disc-based cameras were produced between 1982 and 1990. The Disc 4000 (1982) and the Disc 4100 (1984) are shown above along with a disc cartridge and interior film disc. Shown below are a Minolta and an Ansco version of the disc camera.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disc_film

![]()

![]()
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Ansco

![]()
Kodak Partytime II Kodamatic Instant Camera - 1982. Camera designed for 'instant' photography. It was produced to be given away free at Tupperware parties. Kodak began to manufacture instant cameras in 1977. Polaroid, who had pioneered instant photography in 1948, took legal action. In 1985, after prolonged litigation, judgment went against Kodak who had to discontinue the production of instant cameras and film.
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Kodak_Instant

![]()
Kodak Kodamatic 960 Instant Camera - 1982. Another Kodak instant camera that Kodak was forced to discontinue. Film Size: Kodak HS144 Instant. Shutter: Electronic 1/15 - 1/250. Lens: Fixed 100mm f/12.8. Original List Price: $78.00
www.nwmangum.com/ Kodak/K960-1.html

![]()
Kodamatic 980L Instant Camera - 1982. Similar to the 960, but with auto-focus. Kodak's only auto-focus instant camera. Original MSRP: $115.
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Kodak_Instant

SHARP ELECTRONIC STILL VIDEO CAMERA (ESVC) Prototype - 1982. A photo of this camera has been shown on at least two web sites, however, we have been unable to find any mention of this camera in a Google search, in photo magazines of that time, or on Sharp's very extensive history site. This may have been a quickly made mockup to present to the press to in effect say, "Hey, we are working on one of these too!" At the time of the showing of an actual working still video camera by Sony in August of 1981, the general reaction by other camera manufacturers was stunned silence. Companies that were not thinking of an electronic camera, or perhaps had such a camera on the back burner, were suddenly stirred into action. It was immediately obvious that Sony, an electronics company with a great deal of experience in professional quality video camera production, now had a big jump on many others in the forth-coming electronic still camera market and thus they had better put their own programs into high gear. NOT MARKETED.
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/prototypes-rarities/item/sharp-esvc
JVC GR-C1 - 1983. First VHS single-unit video camcorder. This camcorder used Compact VHS tape which JVC introduced in 1982. This was the same tape as standard VHS and the same recording format, but in a cassette which was only 1/3 the size. This compact cassette could be inserted into in a full-sized VHS adaptor shell so that it could be played back in any VHS machine. In this way, JVC achieved miniaturization without compromising compatibility with older equipment. Immortalized in the movie 'Back To The Future' (photo above on right), it is the original, definitive camcorder.

![]()
KODAK PARTYSTAR Kodamatic Instant Camera - 1983. This particular camera was produced for distribution at Tupperware parties.
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Kodak_Instant



MICRON TECHNOLOGY MICRON BULLET - 1983. A 1984 ad in
Robotics Age stated that the MincronEye (purchased as a unit or in kit
form) camera had a 128 X 256 element resolution (optical RAM) which
could produce a grey scale photo with a plug-and-go
operation. The images were reportedly of very low quality.
Lens: 16mm f/1.4. (TV). MSRP $295-$395.
http://www.theoldrobots.com/images40/Scorpion61.pdf
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/cameras/item/microneye-bullet
STYLING EXERCISE - 1983.
Designed by Luigi Colanie as a still video camera, one of five camera styling
exercises commissioned by Canon in 1983. Luigi Colani is a German who
was born in Berlin in 1928, and is famous for his opinions such as "an egg represents
the highest form of packaging since the dawn of time," or "no straight lines
in the universe." His digicam was to use solid-state memory and
was characterized by the objective lens and viewfinder being on the same axis.
The flash unit was to fire through the objective lens. Exhibited in the
1984 Photokina, the 5 System mockups produced a major sensation. NOT MARKETED.
https://sources.tistory.com/entry/Colanis-concepts-the-future-of-cameras

![]()
CANON NEW SURE SHOT - 1983. The third in Canon's Sure Shot series, released in 1983, this was known as the (New) Sure Shot in the US, AF35M II in Europe, and Autoboy 2 in Japan. Its specifications are very similar to the original Sure Shot (but with a 4-element, 4-group lens this time) but can be identified by the sloped edge near the shutter release button.
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Canon_(New)_Sure_Shot/AF35M_II/Autoboy_2


![]()
![]()
NIMSLO 3D CAMERA - 1983. Jerry Nims and Alan Lo. One of many 3D 35mm cameras produced by various manufacturers over the years. The Nimslo was a stereoscopic camera that took four photos simultaneously on 35mm film which then provided three-dimensional views. Four fixed focus f5.6, 30mm triplet lenses. Shutter 1/30 to 1/500 second. The Museum of the History of Science, Oxford, England. The company that produced the Nimslo was taken over by another company which followed up with the Nishika N8000 3D camera (photo on the right).
http://www.stereoscopy.com/cameras/index.html


![]()
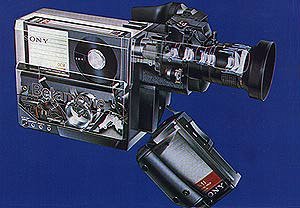
SONY BMC-100/110
- 1983. The Sony BMC-100
(BMC-110 in USA) Betamax was the first consumer model combined camera and recorder to go on sale.


![]()
SANYO VRC 100 - 1983. Other manufacturers produced Beta movie cameras similar to the Sony BMC-100/110 which were then sold under a variety of brand names. Sanyo and Toshiba manufactured store brands for Sears, Marantz, Radio Shack, Rent-A-Beta, Navco, Magnasonic and others. Sony produced units for Zenith and Pioneer. The Sanyo VCR 100 kit came in a nicely fitted aluminum case as well as with a lined vinyl case for the camera itself.
http://www.mrbetamax.com/OtherGuys.htm

![]()
FISHER CAM-500 - 1983. A typical video camera of the 1980s. It used a Saticon direct-readout television pickup tube. Saticon Tubes with a Selenium storage layer were considered suitable for acquiring fast moving images. Their typical charateristics were low lag, excellent resolution, and signal uniformity.
http://yello80s.com/technology/cameras-video-recording/
https://www.servicemanuals.net/FISHER/CAM500-CAM-500/592774/detail.aspx

PENTAX
NEXA - 1983. Pentax demonstrates a
B&W
analog still video camera prototype, the Nexa. Images were stored on a miniture floppy disk. NOT MARKETED.
https://www.aohc.it/catalogo.php?catalogo=oggetti&id_catalogo=113&filtro[tipologia]=16&lingua=it
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/prototypes-rarities/item/pentax-nexa
1980
- 1983