
1970s

![]()
BREMSON / CAMERZ MODEL 10 - Circa 1970. Reference the 1950s page. The Lustre-Pak, a wooden camera, was made by Bremson Photo Industries, Kansas City, Missouri for the purpose of taking high school yearbook photos. The above camera is a later version of their cameras which were rented to photographers, but with the difference that the it was manufactured by Photo-Control Corporation of Minneapolis, MN, for Bremson. Like the previous wood version, the above camera is entirely manual except for the shutter which also has an electronic release. Both used 35mm film and both used a string to allow the photographer to properly judge the distance to the subject, and like Bremson, Photo-Control Corporation is no longer in existence. Both the old and new version are extremely rare, especially in the near mint condition of the above sample. At the time of this writing, one seller had the lens portion without magazine "on sale" for $399.
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Camerz

![]()
YASHICA ELECTRO 35 GS- 1970. The Yashica Electro 35 GS is a coupled-rangefinder, leaf-shuttered 35mm camera with aperture-priority automatic exposure. The Electro 35 GS/GT was released in 1970 by Yashica. The lens is a Color-Yashinon DX 1:1.7 f=45mm lens made in Japan and is identical to the one on the Electro G that precedes it and the GSN that follows it.
http://en.wukipedia.org/wiki/Yashica_Electro_35

EIGHT-INCH FLOPPY DISKETTE - 1970. IBM invented the eight-inch floppy diskette and its drive to improve the distirbution of microcode patches and diagnostics. It was first used in 1971 on the IBM System/370 Model 145. The eight-inch floppy won rave reviews for its reusability, portability, and inexpensive high-density storage capability. Now it would take a hundred thousand of those original eight-inch floppies (80 KB each) to store the same data that many digicamers routinely place onto their 8-GB Compact Flash card. Later versions of the eight-inch floppy had a capacity of about 256 KB (information thanks to David Fiedler).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floppy_disk




FIRST COMMERCIAL SSTV CAMERA AND MONITOR - 1970. Robot Research, Inc. produces the first commercial version of the slow scan TV HAM radio image transmission devices originally developed by Copthorne McDonald in 1957. The company's first products were the 70A monitor (left) and 80A camera (center). Robot Research still produces SSTV equipment today and their products are used by many HAM operators. The Kenwood handheld VC-H1 is also popular for amateur radio transmission of images (see 1998). Products of both companies can frequently be found on eBay.
http://www.astrosurf.com/luxorion/qsl-ham-history12.htm
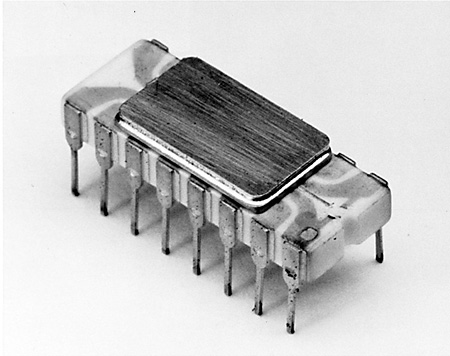




INTEL 4004 MICRO PROCESSOR - 1971. In November, 1971, Intel publicly introduced the world's first single chip microprocessor, the Intel 4004, invented by Intel engineers Federico Faggin, Ted Hoff, and Stan Mazor (left to right above). The 4004 contained 2250 transistors on a single chip.
http://www.computerhistory.org/exhibits/internet_history/internet_history_70s.shtml
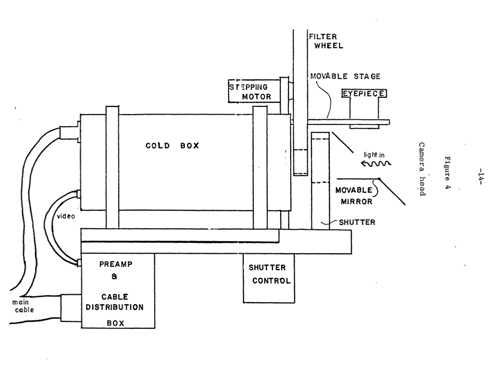
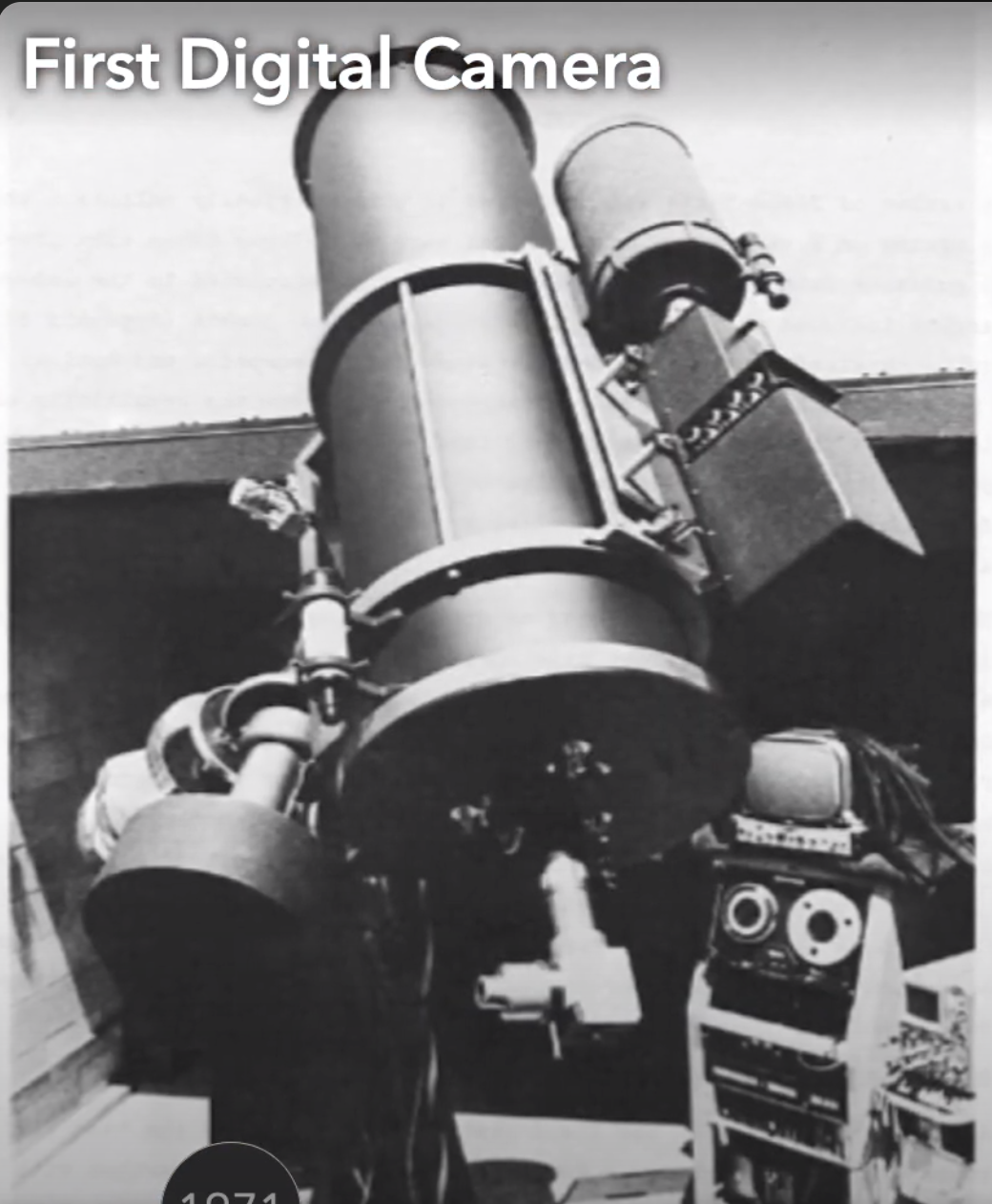

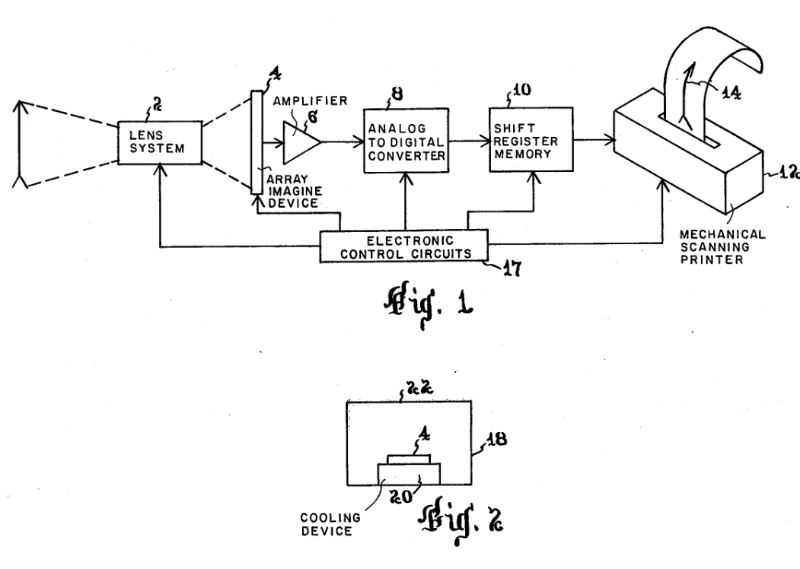
MCCORD/WESTPHAL DIGITAL ASTRONOMY PHOTOGRAPHY PROJECT - 1971. Dr. Roger Clark submitted information concerning the use of equipment in 1971 and thereafter to produce digitized photographs of the moon and other astronomical objects. The camera head involved in the operation consisted of a silicon target of a vidicon tube which was scanned by an electron beam thereby producing an electrical signal that was then digitized and stored on tape. The electronics and tape recorder were mounted in a 53-cm electronics rack and the camera was attached to the rack by a cable.
This raises an interesting question, when should a photography system be described as digital photography? That is, if a series of independent components are used to first capture an analog image and then convert it into a digital image, should such a system be described as a digital camera? Where exactly do we draw the line between analog photography and digital photography? In general, this may not be a question of consequence except when the matter of who developed the first digital camera arises. I am not qualified to be the arbiter in such matters, so I merely present the material and viewers can come to their own conclusions.
To make matters a little more confused, I refer viewers to the bottom of my 1900-1920 page and the Bartlane Transmisson System. That system converted black and white photos into digits representing several shades of gray, and then transmitted the data via punched tape where the photos were then reconstructed on the other end. Strictly speaking, that system was a form of digital photography and could fairly be called the first instance of digital photography, or at least digital scanning.
The schematic shown above of the camera head is from a thesis by Jay Stuart Kunin which describes the McCord/Westphal project in detail.
Dr. Clark has a great deal of instructional material on his home page, so much so that it serves as a complete one stop location for everything having to do with digital photography.
After reading the material submitted by Dr. Clark, perhaps you would like to express your own opinion as what is a digital camera and who should get the credit for the first such camera.
Thesis
http://www.clarkvision.com/articles/first.digital.camera/
The first Digital Camera: 1971, by Dr. Rodger N. Clark
http://www.clarkvision.com/index.html
Home Page, Dr. Roger N. Clark


 THE FIRST E-MAIL
- 1971. QWERTYUIOP, these letters
(or something similar) made up the first message to be sent electronically over
e-mail. If the letters looks familiar, it's because they make up the top
row of the standard keyboard. The person responsible for the first e-mail
was Ray Tomlinson, a computer engineer. Tomlinson was employed by Bolt
Beranek and Newman, a company contracted by the United States Defense Department
in 1968 to build ARPANET, the precursor to the Internet. Before the first
message could be sent Tomlinson needed to come up with an address.
He chose the @ symbol to distinguish addresses to mailboxes in a local machine
and messages that were to be sent out onto the network. Tomlinson says
that he chose the @ symbol because it wasn't a person's name and for it's symbolic
meaning, at; someone@someplace. The first two machines to communicate
via email were actually sitting right next to each other, both connected to
the ARPANET. At that time, computers communicated through a separate
computer on the ARPANET network. This was where the transfer of "QWERTYUIOP"
took place. Within two years seventy-five percent of ARPANET traffic was
e-mail.
THE FIRST E-MAIL
- 1971. QWERTYUIOP, these letters
(or something similar) made up the first message to be sent electronically over
e-mail. If the letters looks familiar, it's because they make up the top
row of the standard keyboard. The person responsible for the first e-mail
was Ray Tomlinson, a computer engineer. Tomlinson was employed by Bolt
Beranek and Newman, a company contracted by the United States Defense Department
in 1968 to build ARPANET, the precursor to the Internet. Before the first
message could be sent Tomlinson needed to come up with an address.
He chose the @ symbol to distinguish addresses to mailboxes in a local machine
and messages that were to be sent out onto the network. Tomlinson says
that he chose the @ symbol because it wasn't a person's name and for it's symbolic
meaning, at; someone@someplace. The first two machines to communicate
via email were actually sitting right next to each other, both connected to
the ARPANET. At that time, computers communicated through a separate
computer on the ARPANET network. This was where the transfer of "QWERTYUIOP"
took place. Within two years seventy-five percent of ARPANET traffic was
e-mail.
http://gunkelweb.com/coms465/email/firstemail.html


CASIO
PHONE-MATE 400 - 1971 - Casio created the telephone answering device
(TAD) industry by introducing the first commercially viable answering
machine. The Phone-Mate was built around a standard off-the-shelf box
made of pressed sawdust covered with wood grain plastic. The size of
the box was determined by the minimum amount of space necessary to
contain two small reel-to-reel tape recorders and the necessary
electronics to make it into a telephone answering machine. It was
powered by four D-cell batteries and could record twenty messages
before having to be rewound. MSRP $300.
https://www.watchprosite.com/horological-meandering/time-flies-by--or-does-it-/17.1028423.7315243/
http://resume.wizzard.com/w1998/casiophonemate/corp.html
https://spectrum.ieee.org/the-consumer-electronics-hall-of-fame-phonemate-400
https://www.askqotd.com/the-answering-machine/


![]()

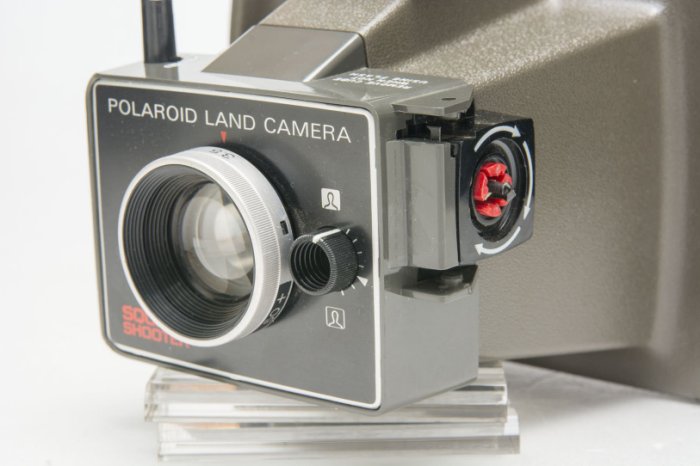
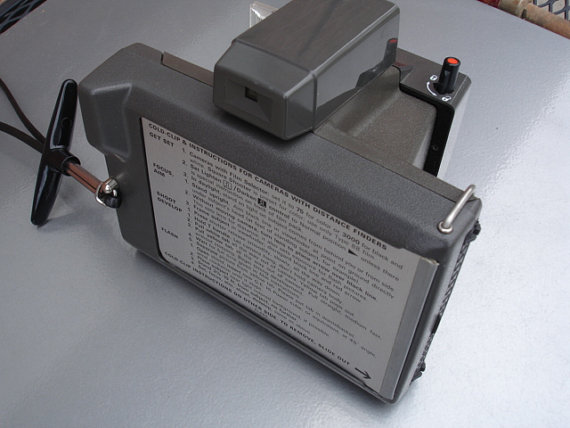
POLAROID SQUARE SHOOTER - 1971.
Originally produced between 1971 and 1972, the Square Shooter was a
Ridged Plastic Bodied, Packfilm Type 80 instant camera.
Although similar to the Colorpack II the Square Shooter was
considered more advanced and that was reflected in the retail price of
$34.95 as opposed to the Colorpack II retail price of
$29.95. It lacked the built-in development timer of
the Colorpack II and was slightly smaller. Camera
donated by our beautiful daughter, Tatiya, who seldom misses a garage
sale in our area (sorry guys, she's already married).
The Square Shooter featured:
A built in socket for Hi-Power flashcubes, a "Focused Flash" system.
Triangulation distance finder.
Exposure system designed only for 75 ASA films.
Typically they also featured the adjustable front cell focusing lens with distance scaling marked on the lens ring.
"Everset" shutter that did not need re-cocking.
http://camerapedia.wikia.com/wiki/Polaroid_Square_Shooter

![]()
Canon Canonet 28 - 1971-76. Lens
f/2.8 40 mm. Shutter 1/30 - 1/620 sec. MSRP with case $64 US (about
$345 in 2010 dollars). It was purchased on eBay in excellent condition
for $10.
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Canon_Canonet_28


![]()
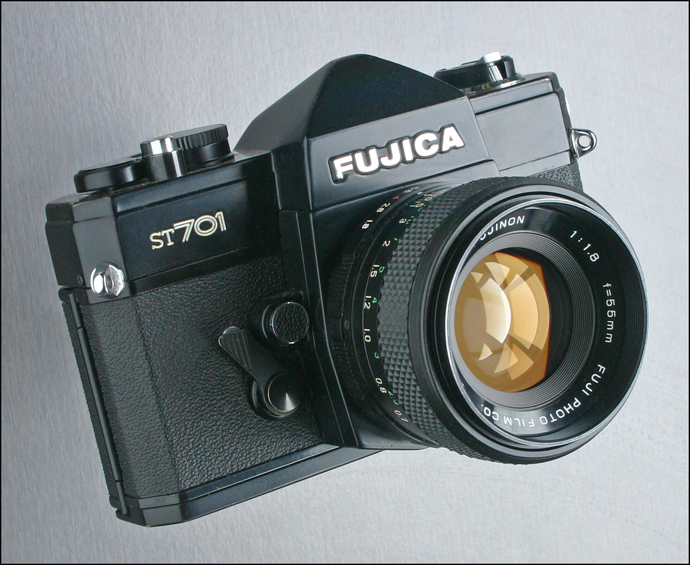
FUJICA ST701 - 1971. The Fujica ST701 was the first camera using a silicon photo-cell receptor coupled to a field effect transistor (FET) circuit for light metering. The FET photo cell provided higher sensitivity, instantaneous response and more precise measurement of light compared to Cadmium-Sullfide (CdS) photo-cells used by other cameras at that time. The mercury batteries (1.35 volts) originally sold with the ST701 are no longer available. Owners should replace the old batterie with zinc/air cells of 1.35 volts such as Everready 675. Do not use alkaline cells of 1.55-1.6 volts because they will not work in the ST701. It may be necessary to to wrap the new batteries with tape or paper as they will probably be smaller in diameter than the original batteries. The ST701's f/1.8, 55 mm lens is considered to be of very good quality. The ST701 was also available with a chrome top in addition to the black top shown above. A camera similar to the one shown above with f/1.8, 55 mm lens and case was purchased on eBay in very good to excellent condiiton for $10.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fujica
![]()
PENTAX SPOTMATIC SPIIA - 1971. Manufactured by Asahi Optical Company. Model SPIIa sold in USA only as the Honeywell Pentax SPIIa. Shutter 1 second to 1/1000 second. Cds TTL metering. Pentax screw mount. Lens: Super Takumar 1:1.4 50mm. F/1.4 - 16.
The Spotmatic SP II added the following features to the Spotmatic SP:
Switch for hot shoe (FP and X)
Roller on film door for better tracking of film
Improved shutter
Modified self timer
Modified meter and switch (greater EV range)
Increased ASA range
Shape of top cover
Brighter view finder
The above camera was donated to DigiCamHistory.Com in near mint
condition by Ron Hardwick, one of Ohio's top professional golf instructors.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pentax_Spotmatic
http://www.photoethnography.com/ClassicCameras/AsahiPentaxSpotmaticSPII.html
http://www.pentaxforums.com/camerareviews/pentax-spotmatic-iia.html
ONE-STEP INSTANT PHOTOGRAPHY, Polaroid SX-70 - 1972. The Polaroid SX-70 Land camera is introduced - the first fully automatic, motorized, folding, single lens reflex camera which ejected self-developing, self-timing instant color prints. Many consider the SX-70 to be Dr. Land's masterpiece. Original MSRP $180. The above kit in very good to excellent condition was obtained on eBay for $49, however, some vendors are currently (fall, 2010) askng as much as $390 for the same item. There are a great many SX-70s available on eBay, so be selective in your choice.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polaroid_SX-70


![]()
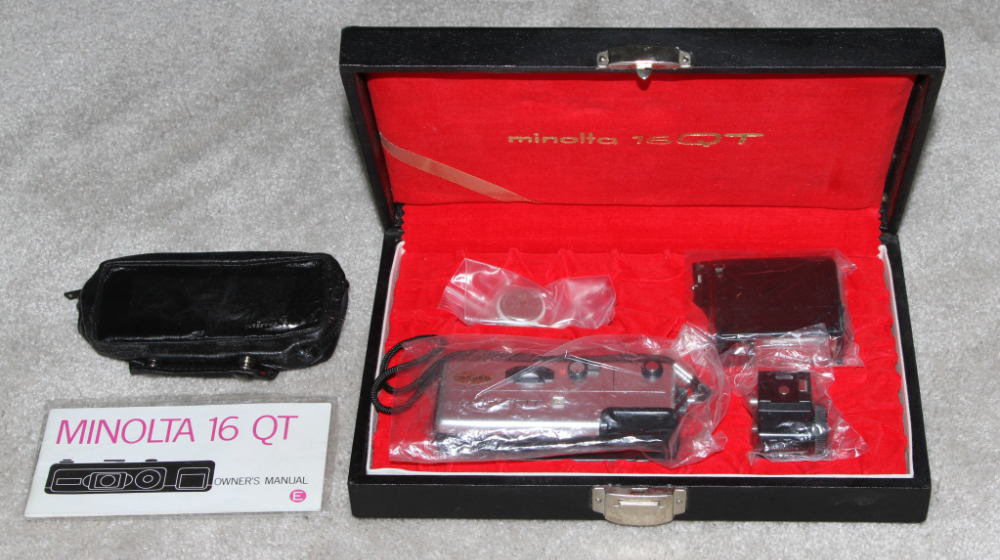
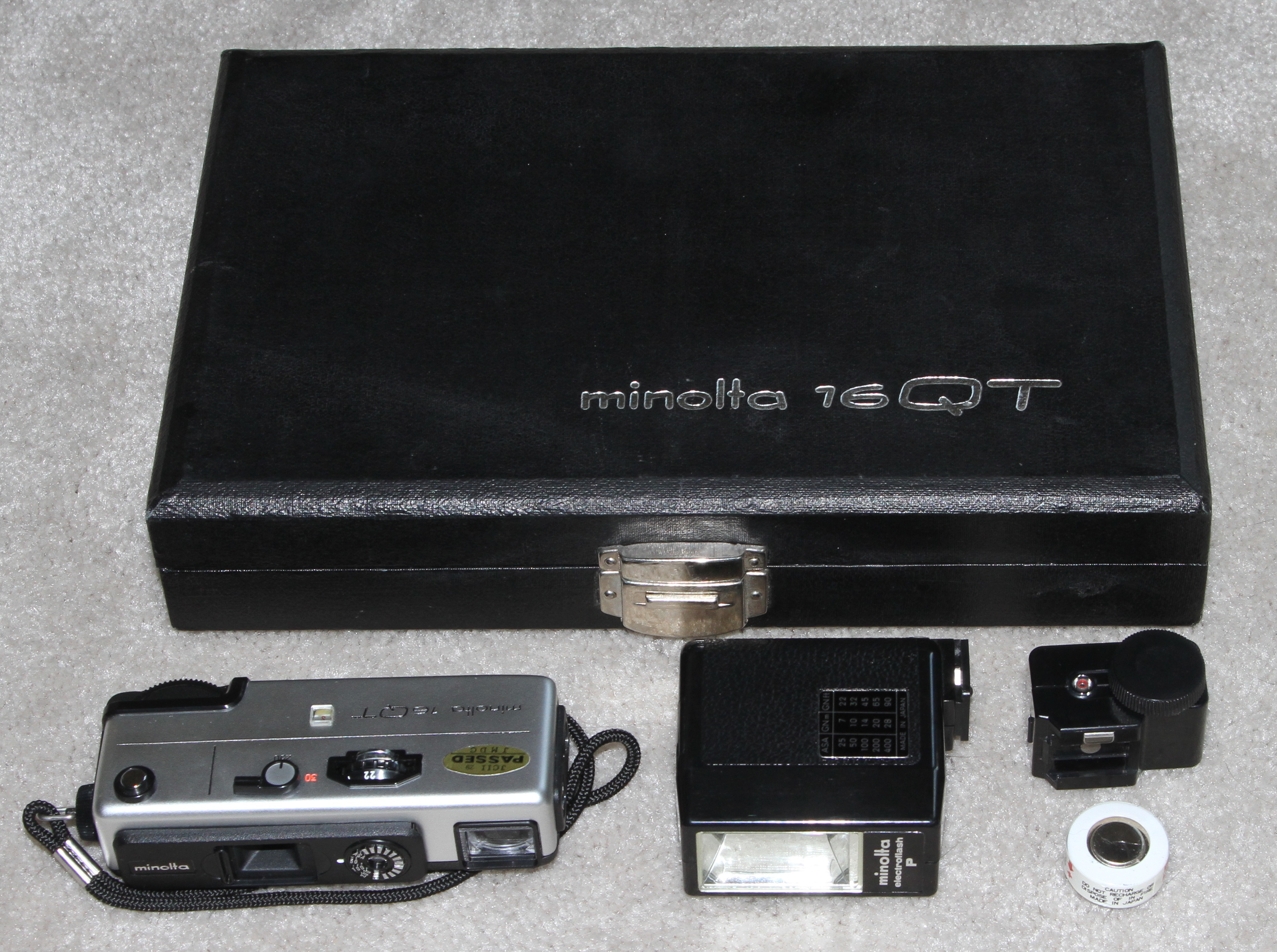
MINOLTA 16QT -1972. Most 16mm cameras of the time were inexpensive with very few features. The Minolta 16 QT was the last camera made for Minolta's 16mm film cartridges and had many features most other 16mm cameras did not have. Frame size: 12 x 17mm, two speed shutter and three element triplet lens. Lens focused from 1.2m to infinity. The 16 QT had many unusual features for a 16mm camera: The viewfinder had three different indicators: a red transparent tab that indicated the current focus distance, a red warning bar to indicate that the camera was set to the slow speed, and lights to indicate over- and under-exposure. The viewfinder was an Albada type, with bright parallax-correcting frame-lines for distance and close-focusing. Shutter speeds: 1/250th and 1/30th, with flash sync at either speed. Apertures: f:3.5 to f:22. The QT accepted Minolta close-up lenses, filter, flash and viewing accessories, including a screw-on hot shoe that accepted standard flashes and offered a PC-socket pass-through. Chrome or black versions were available. MSRP: 45.95 British pounds. This 50-year old camera was purchased in August of 2022 in like new condition.
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Minolta_16_QT
http://www.subclub.org/shop/minolta.htm
ONE-STEP INSTANT PHOTOGRAPHY, Polaroid SX-70 - 1972. The Polaroid SX-70 Land camera is introduced - the first fully automatic, motorized, folding, single lens reflex camera which ejected self-developing, self-timing instant color prints. Many consider the SX-70 to be Dr. Land's masterpiece. Original MSRP $180. The above kit in very good to excellent condition was obtained on eBay for $49, however, some vendors are currently (fall, 2010) askng as much as $390 for the same item. There are a great many SX-70s available on eBay, so be selective in your choice.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polaroid_SX-70

 FIRST
U.S. ELECTRONIC PHOTOGRAPHY SYSTEM PATENT - 1972. Texas Instruments patented a film-less electronic camera.
Inventor: Willis A. Adcock; (Dallas, TX). Assignee:
Texas Instruments Incorporated (Dallas, TX). Filed: June 27, 1972
and again on October 29, 1976 and June 23, 1977. Abstract : "A completely
electronic system for recording and subsequently displaying still life pictures
includes an optical-electronic transducer for generating electronic signals
responsive to an optical image. The signals are stored and subsequently applied
to a visual display. Means are provided for applying the signals at a scan rate
synchronized with the scan rate of the display to effect a stationary display
of the optical image. Preferably, the display is a conventional television set."
FIRST
U.S. ELECTRONIC PHOTOGRAPHY SYSTEM PATENT - 1972. Texas Instruments patented a film-less electronic camera.
Inventor: Willis A. Adcock; (Dallas, TX). Assignee:
Texas Instruments Incorporated (Dallas, TX). Filed: June 27, 1972
and again on October 29, 1976 and June 23, 1977. Abstract : "A completely
electronic system for recording and subsequently displaying still life pictures
includes an optical-electronic transducer for generating electronic signals
responsive to an optical image. The signals are stored and subsequently applied
to a visual display. Means are provided for applying the signals at a scan rate
synchronized with the scan rate of the display to effect a stationary display
of the optical image. Preferably, the display is a conventional television set."
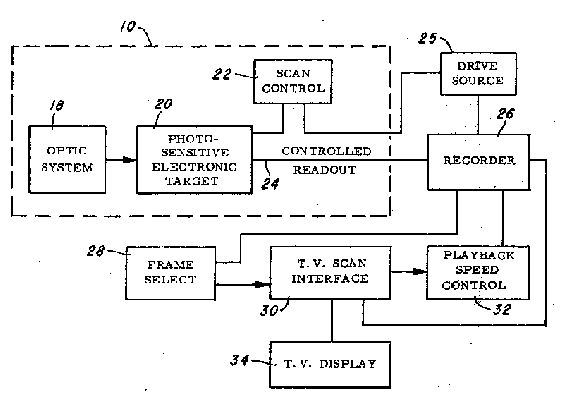
Schematic Diagram of Willis Adcock's Electronic
Photography System
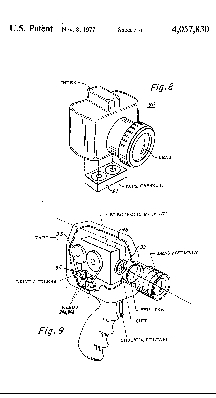
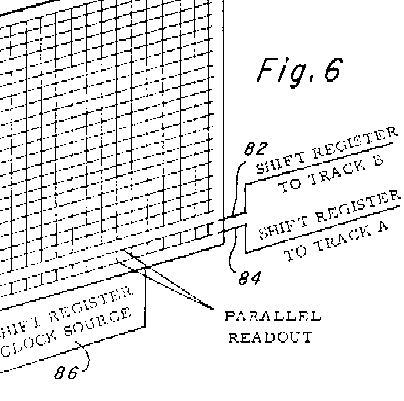
Proposed Camera Designs (Note Tape Drives), and Portion
of CCD Sensor Design
The computerized patent office filing system only extended back to 1975 at the time of this posting, however, the refilings made in 1976 and 1977 are essentially the same as the original 1972 application and can be viewed in their entirety, including drawings, by doing a patent search. To perform this search, go to the patent office's web site shown below and select "Patents" in the drop-down menu. When the patents' page appears, select "Quick Search." On the quick search page place the patent number in the "Term 1" box and select "Patent Number" in the "Field 1" (4,057,830 or 4,163,256) box. In the "Select years" box select "All years" and press the search button. To view the patent drawings, which are TIFF images, you must first download TIFF plug-ins which are free.
For PCs use:
AlternaTIFF: http://www.alternatiff.com/(tested: IE, Netscape, Opera)
For the Apple Macintosh Apple's freely distributed
Quicktime version 4.1 or later works, but does not provide printing capability.
It is available from the Apple Web site at: http://www.apple.com/software/.
For Linux, a plug-in called "Plugger" works with
Netscape Communicator�. It is available at: http://fredrik.hubbe.net/
The U.S. Patent Office web site is at: http://www.uspto.gov
Date reference: http://inventors.about.com/library/inventors/bldigitalcamera.htm

![]()

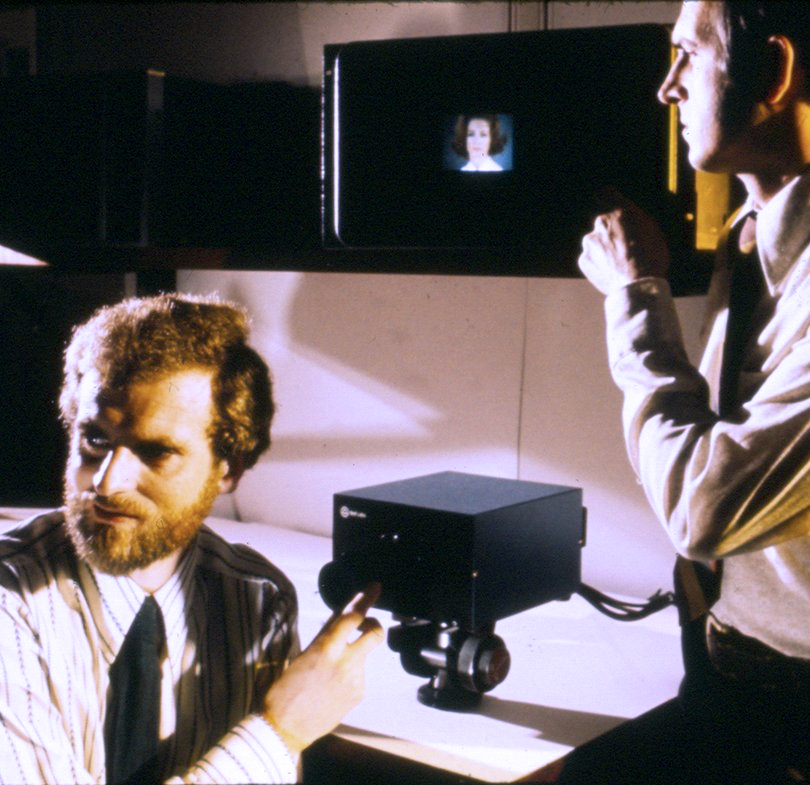
FIRST CCD TV VIDEO CAMERA - 1972. Using the Smith & Boyle CCD, Bell Labs researchers built the world's first solid-state video camera in 1972. Left - Mike Tompsett and Ed Zimany test the new solid state camera. Right - image of Mke Tompsett's wife. In 1975, Bell Labs demonstrated the first solid-state camera with image quality sharp enough for broadcast television. We believe we were the first digital camera history web site to provide a photo and information concerning this camera.
https://www.bell-labs.com/timeline/#/2010/1/closed/
http://www.dpreview.com/articles/6715926949/boylesmith


RCA PROTOTYPE CCD TV CAMERA - 1972. The
camera used a CCD from Bell Labs with 32 x 44 pixels.
https://www.tvcameramuseum.org/earlyccd/rca/rcacam1a.html
http://www.oldradio.com/archives/hardware/TV/RCA-TV.htm
http://www.researchgate.net/publication/3073504_Single-chip_color_camera_using_a_frame-transfer_CCD


![]()
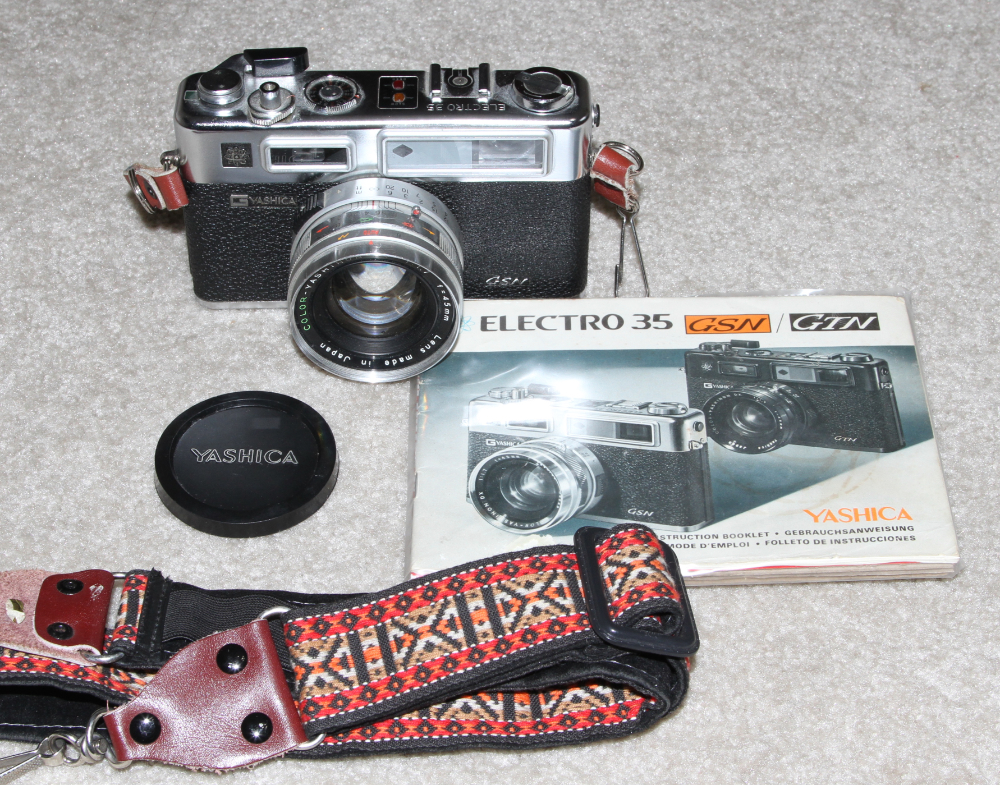
YASHICA ELECTRO 35 GSN- 1973.
The design of the Yashica Electro GSN essentially goes back to the
first Electro 35 rangefinder released in 1965 and was not changed until
the end of the production of the GSN in 1987. Its size is comparable to
that of the Konica Auto S2 and the elder Minolta Hi-Matic models 7S, 9,
and 11. It had a fast 1:1.7 45mm lens. There is a similar black
finished model called Electro 35 GTN.
http://en.wukipedia.org/wiki/Yashica_Electro_35

![]()
FIRST
COMMERCIAL CCD - 1973. Fairchild Imaging successfully
developed and produced the first commercial charge coupled device in 1973 with
a size of 100 x 100 pixels. In 1974,
the above Fairchild CCD and an 8-inch Celestron telescope were used by James R. Janesick to produce the first astronomical
CCD image (see James R. Janesick below). It was also used in the world's first known operational
electronic CCD still image camera which was constructed by Steve Sasson of Kodak
(see farther down on this web page). The above CCD was donated to DigiCamHistory.Com by Jim Janesick.


FAIRCHILD MV-100 - 1973.
The Fairchild MV-100 had the same 100 x 100 pixel CCD as the below
MV-101 and was the first commercially available CCD camera.
Although it used a CCD imager, photos for the MV-100 and MV-101 below
were recorded in analog, not digital (https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/cameras/item/fairchild-mv-101).
https://www.tvcameramuseum.org/earlyccd/fairchild/mv100p1.html



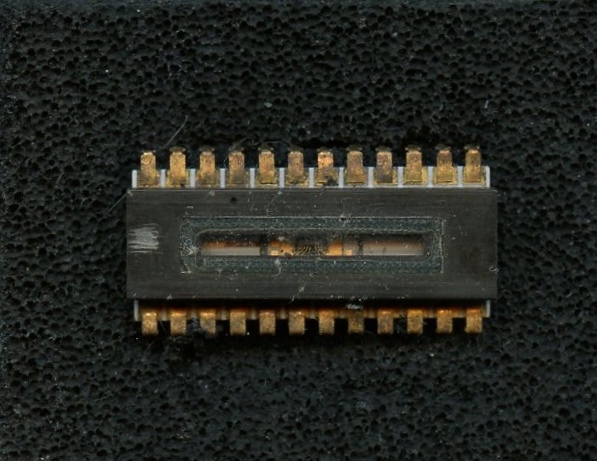
![]()

FAIRCHILD MV-101 - 1973. The MV-101 was about 76mm in diameter
and
48mmin length (without lens).
The above 1x128 pixel experimental CCD was developed by
Fairchild. The Fairchilld
CCD 101 was donated to DigiCamHistory.Com by James R. Janesick.
https://www.tvcameramuseum.org/earlyccd/fairchild/mv100p1.html
(1) . The Fairchild MV-101 was used to perform Procter & Gamble
product
inspections and was also used in the world's first still
image digital camera hand-built by Steve Sasson of Kodak - see article
below: KODAK PROTOTYPE CCD DIGITAL CAMERA - 1975. MSRP $4,000.
See 1981 page, UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FAIRCHILD ALL-SKY CCD CAMERA - 1981, for use of the Fairchild CCD by the University of Calgary in their All-Sky camera. Television
(2) Applications of
interline-Transfer CCD Arrays, Kenneth A. Hoagland,
1976 (Fairchild Corp.), page 154 (This article is available on the
Internet as a PDF document:
http://www.imagesensors.org/Past%20Workshops/Marvin%20White%20Collection/1976%20Papers/1976%2022%20Hoagland%20INCOMPLETE.pdf
(3) From Presentation by K. W. White, Electronic Imaging International Conference, 1993. The
article by K. W. White discussing the use of the Fairchild MV-101
camera to perform Procter & Gamble product inspections is no longer
available on the web, but may be purchased from the German National
Library of Science and Technology
(4) TV Technology On Display in New York: by Stephen Traiman. Lincoln Center. "Pocket-sized solid-state camera shown by Farichild" (MV-101 CCD-charge coupled device at $4,000). Billboard, 8 February 1975, page 47.


Questar astronomical CCD telescope
Celestron astronomical CCD telescope

Fairchild 100 x 100 area array (CCD201ADC)
Questar modified Nikon F camera

Fairchild linear 1 x 128 CCD (CCLID-60A)
Vidicon tube
CCD collection
http://www.digicamhistory.com/Spacecraft%201960s%20and%2070s.html
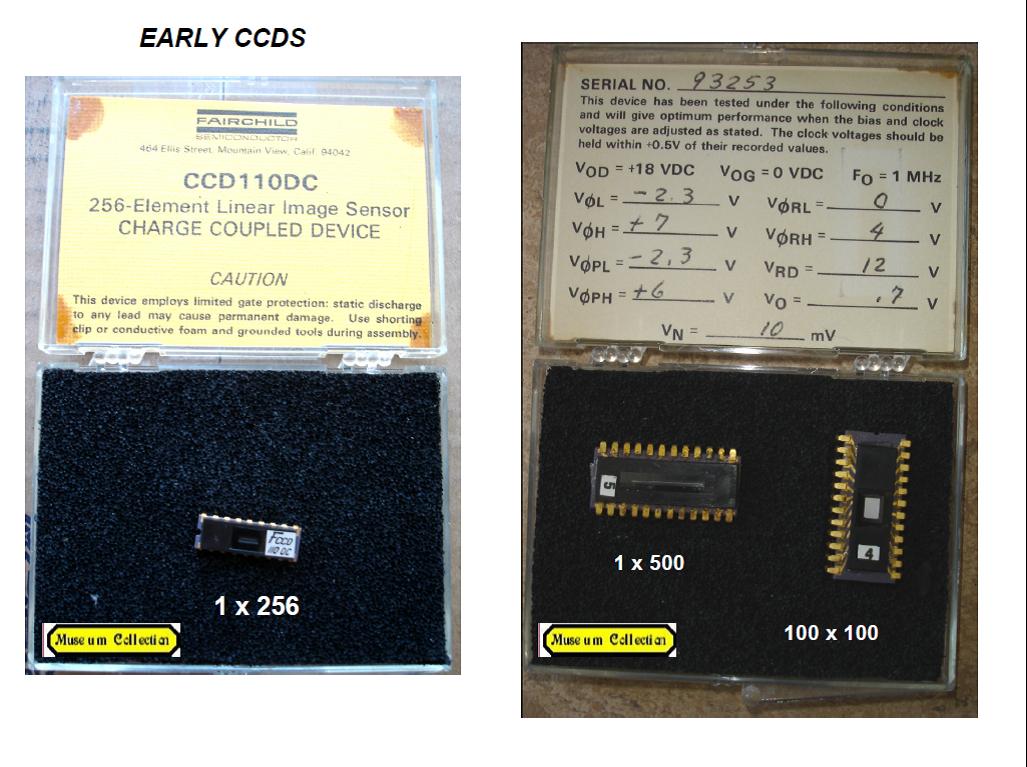
Fairchild linear 1 x 500 CCD
Fairchild linear 1 x 256 CCD (CCD110DC)
........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
For more on James Janesick, CCD technology and use of CCDs in space click here
...........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................

![]()
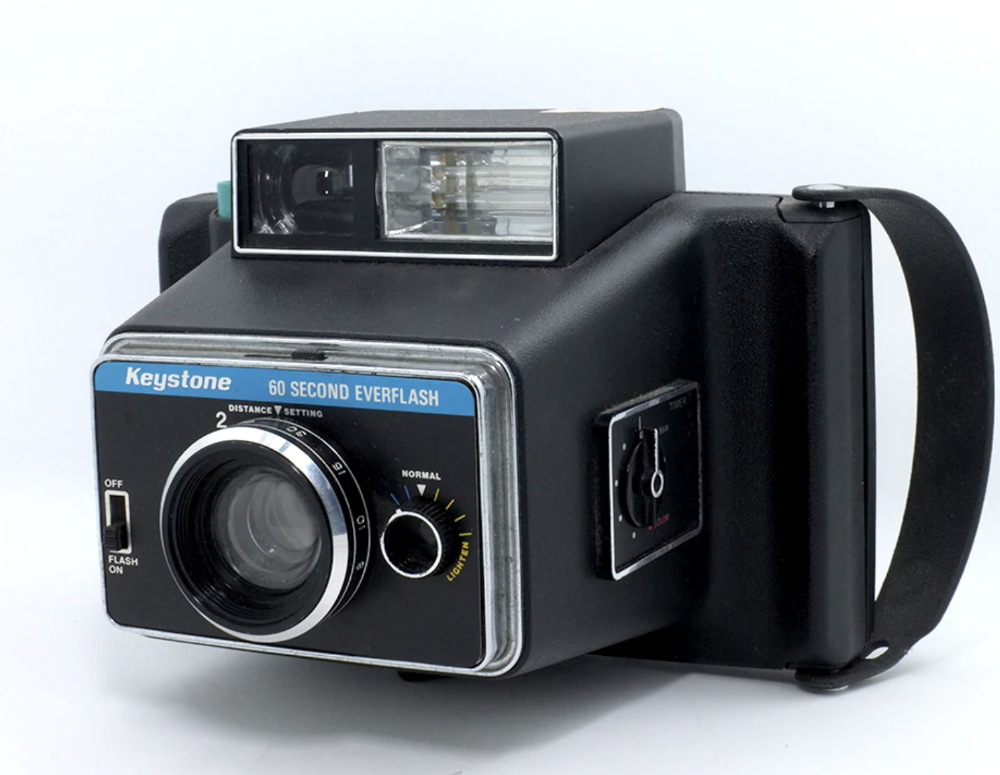
KEYSTONE MODEL 800 Instant Camera - 1975.
The Keystone Camera Company, a division of the Keystone
Manufacturing Co., was founded in Boston, Massachusetts, circa 1910.
They were an American manufacturer of consumer photographic equipment.
Notable products were movie cameras, 126
cartridge and 110 cartridge cameras with built in
electronic flash (the "Everflash" series). In the 1930's, they made
inexpensive 8mm and 16mm movie cameras that are still in use today.
They were acquired by Berkey Photo, Inc. in 1966. In 1978, Berkey sold
its camera division and thus abandoned this market. The Keystone Camera
Company filed for chapter 11 protection in January 1991. Later in 1991,
they were purchased by Concord Camera Company. The instant
cameras made by Keystone, unlike Kodak instant cameras, used Polaroid
types 88, 107 and 108 film packs, thus were not objected to by the
Polaroid Corporation. Automatic film exposure, shutter 1/500 to
10 sec, flash and timer. Original MSRP $79.95
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Keystone_Camera_Company
http://camerapedia.wikia.com/wiki/Keystone_Everflash


CCD FABRICATION - 1974.
Dr. Gil Amelio conceives a fabrication process that allows CCDs to be produced
on a conventional wafer fabrication line.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gil_Amelio
http://www.aavso.org/files/ccd_school_2.pdf






![]()
SONY AVC-3250 - 1974. The AVC-3250 was used in many schools and corporate video studios of the time. Two thirds-inch vidicon tube for pickup, detachable four-inch CRT viewfinder for aiming. Lens: f 1.8, 12.5mm - 75mm. 6 to 1 zoom. This camera and others in the series were the work horses of their day. For those interested, a fine collection may be established sticking just to video cameras. See the web site below for an idea of items available. The above camera with two lenses and case with accessoiries, all in excellent conditon, were purchased on eBay for just $76.
http://www.labguysworld.com/Sony_AVC-3250.htm
Shown below is the Akai VC-115 studio videocamera which was used for much the same purposes as the Sony AVC-3250.

![]()


![]()
TEAC HC-100 - 1974. Shown above is a TEAC video camera similar to the Akai VC-115 , the HC-100. For those collectors looking for a specialty area, early vidoe cameras and camcorders are plentiful in excellent condition and at bargain basement prices. This HC-100 in with fitted cased was obtained on eBay for only $20.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TEAC_Corporation

![]()
KODAK XL 340 - 1974. One of the many amateur movie cameras marketed by Kodak over the years that can now be purchased by the collector in excellent condition very inexpensively . Film: Super 8 cartridge. Shutter: 9, 18 frames per second. Lens: Manual focus Ektar 9-21mm f/1.2
http://super8wiki.com/index.php/Kodak_XL_340
http://www.usedprice.com/items/camera/kodak/super8-movie-camera/xl340-81793.html


![]()
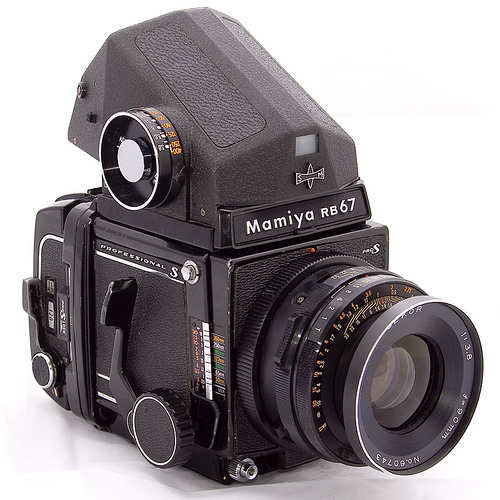
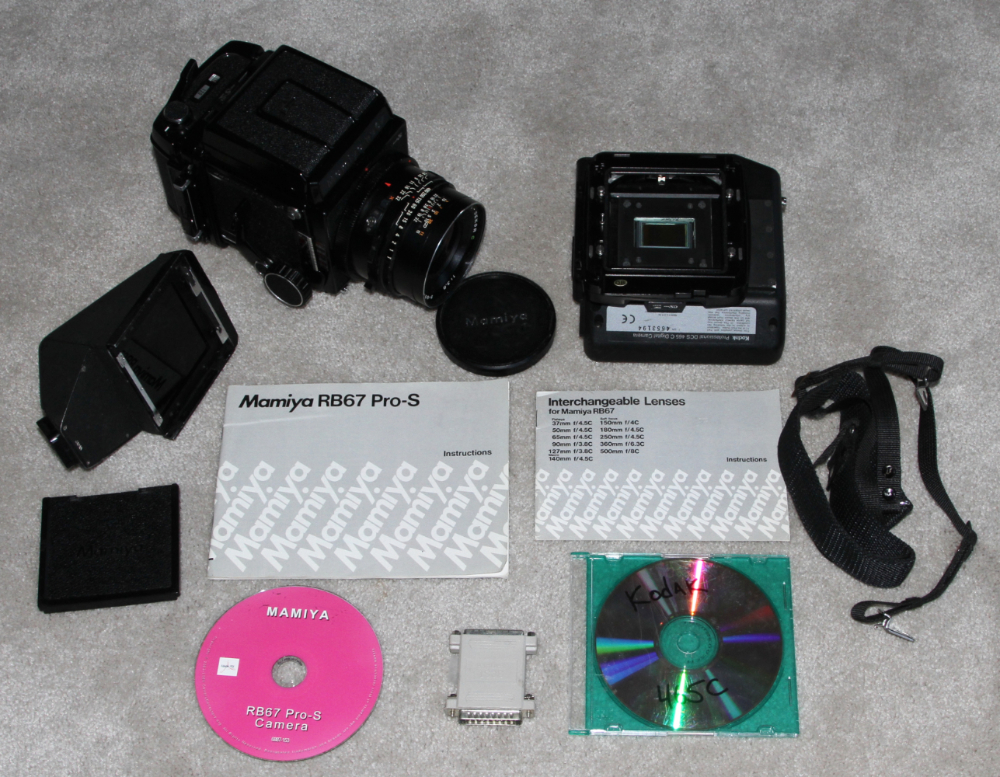
MAMIA RB67 PRO S - 1974. Medium
foremat (6 x 7 cm) camera. The RB67 had a rotating back which enabled
photographs to be taken in either landscape or portrait orientation
without rotating the camera, a very valuable feature for studio cameras
mounted on heavy tripods. . The RB67 soon became widely used by
professional studio photographers. In 1995 Kodak marketed the Kodak
463c (color) and 465m (monotone) digital backs for the RB67 (photo on
the right). About 200 digital backs were produced of varios
types- color, B & W, and Infrared. MSRP $27,500 for the
digital back ($57,000 in 2024 dollars). Although only about 200
Kodak digital backs were marketed, we were able to purchase the above
sample for a small fraction of what some sellers are now demanding for
cameras that sold in numbers of 1,000 or more.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mamiya
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/cameras/item/kodak-dcs-465
https://beyondtheaperture.com/2020/03/review-mamiya-rb67-professional-s-medium-format-film-camera/


TOSHIBA IK-12 - 1974. The world's first single-tube color consumer video camera.
http://toshiba-mirai-kagakukan.jp/en/learn/history/ichigoki/1973color_camera/index.htm



![]()
POLAROID / USI INC. M500 PASSPORT / ID SYSTEM - 1975. Polaroid
has marketed a great many different instant photo products over the
years, many of which are not known to the general public because they
were sold for industrial/scientific or medical purposes. Some of
these appear on eBay from time-to-time. The M500 ID system kit
contained a camera capable of taking four instant photos at one time,
four of the same photo, two photos of two, or four different
photos. The camera had a built-in flash and variable exposure
system. This early model kit included the Polaroid M500
mountable camera, mounting stand, photo die cutter, heat laminator,
supplies and carrying case. The system was produced in
conjunction with USI Inc., a producer of laminating products and other
office equipment. This particular sample appears to have had
little or no use as all items in the set are in mint condition.
The stand appears to have never been removed from its stow-away
position and the carrying case does not have the usual scratches and
abrasions normally present indicating that it has been moved
about.
https://prezi.com/nz_wji4ih5ky/the-evelution-of-camera/


SATCOM 1 - 1975. SATCOM
1, America's first commercially available geo-stationary satellite was
placed into orbit by a Delta rocket December 12, 1975. Geo-stationary
means that the satellite was placed at a distance above the earth's surface
and over the equator where it would revolve around the earth within the exact
same time period that it takes for the earth to rotate on its axis (synchronous
orbit). This causes the satellite to stay continually above the same point
over the earth's surface so that satellite receivers do not have to follow a
moving satellite. It also means that spy satellites can view the same
area of the earth's surface twenty-four hours a day.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satcom_%28satellite%29
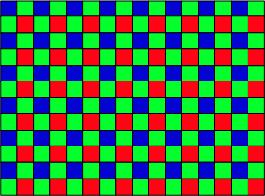


BAYER COLOR FILTER ARRAY - 1975. Bryce
Bayer invented the color filter array that bears his name (the Bayer
filter), which is incorporated into nearly every digital camera and
camera phone on the market today. Described in U.S. Patent 3,971,065,
"Color Imaging Array," filed in 1975, color filters are arranged in a
checkerboard pattern to best match how people perceive images, and
provide a highly detailed color image. The Bayer Filter enables a
single CCD or CMOS image sensor to capture color images that otherwise
would require three separate sensors attached to a color beam splitter
- a solution that would be large and expensive. The red, green, and
blue colors of the Bayer filter are fabricated on top of the
light-sensitive pixels as the image sensor is manufactured, a process
pioneered by Kodak. The drawing on the right of Mr. Bayer's photo
is from his notebokk where he first describes the Bayer system color
sensor array.
http://www.dpreview.com/news/0911/09111701brycebayerhonor.asp

 BETAMAX SL-6200/6300, LV-1801/1901 - 1975.
On 16 April 1975 Sony announced the SL-6300 Betamax VCR deck and the
LV-1801 TV/VCR combination incoporating the SL-6300 and an 18-inch
trinitron color television. On 10 May 1975 Sony aonnounced the
LV-1901 with a 19-inch Sony Trinitron color TV and an SL-6200 Betama
VCR deck. These were the first successful consumer
videocassette. The first Betamax product released in the United
States, the combination LV-1901 TV/VCR floor model, appeared in
November 1975 priced at $2295. The one hour Betamax cartridges
were considerably smaller than the earlier U-matic cartridges, and the
system derived its name from the resemblance of the tape path inside
the mechanism to the Greek letter "Beta"
BETAMAX SL-6200/6300, LV-1801/1901 - 1975.
On 16 April 1975 Sony announced the SL-6300 Betamax VCR deck and the
LV-1801 TV/VCR combination incoporating the SL-6300 and an 18-inch
trinitron color television. On 10 May 1975 Sony aonnounced the
LV-1901 with a 19-inch Sony Trinitron color TV and an SL-6200 Betama
VCR deck. These were the first successful consumer
videocassette. The first Betamax product released in the United
States, the combination LV-1901 TV/VCR floor model, appeared in
November 1975 priced at $2295. The one hour Betamax cartridges
were considerably smaller than the earlier U-matic cartridges, and the
system derived its name from the resemblance of the tape path inside
the mechanism to the Greek letter "Beta"
http://www.cedmagic.com/history/betamax-lv-1901.html

 FIRST
CCD FLATBED SCANNER TO READ TEXT WRITTEN IN ANY NORMAL FONT- 1975. Invented
by Kurzweil of Computer Products using the first integrated chip.
Ray Kurzweil and his team at Kurzweil Computer Products created the
Kurzweil Reading Machine and the first omni-font OCR (Optical Character
Recognition) technology. They did this work in support of
individuals who are blind. The world's first commercially viable
flatbed scanner was developed later in 1984 by Samir Lehaff of Eskofot
inDenmark (information provided by Ron Tussy of The Imerge Group).
FIRST
CCD FLATBED SCANNER TO READ TEXT WRITTEN IN ANY NORMAL FONT- 1975. Invented
by Kurzweil of Computer Products using the first integrated chip.
Ray Kurzweil and his team at Kurzweil Computer Products created the
Kurzweil Reading Machine and the first omni-font OCR (Optical Character
Recognition) technology. They did this work in support of
individuals who are blind. The world's first commercially viable
flatbed scanner was developed later in 1984 by Samir Lehaff of Eskofot
inDenmark (information provided by Ron Tussy of The Imerge Group). 

ALTAIR 8800 HOME COMPUTER - 1975. The Mits Corporation introduced the first popular home computer, the Altair. The Altair computer kit sold for about $400 and began the personal computer revolution.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Altair_8800
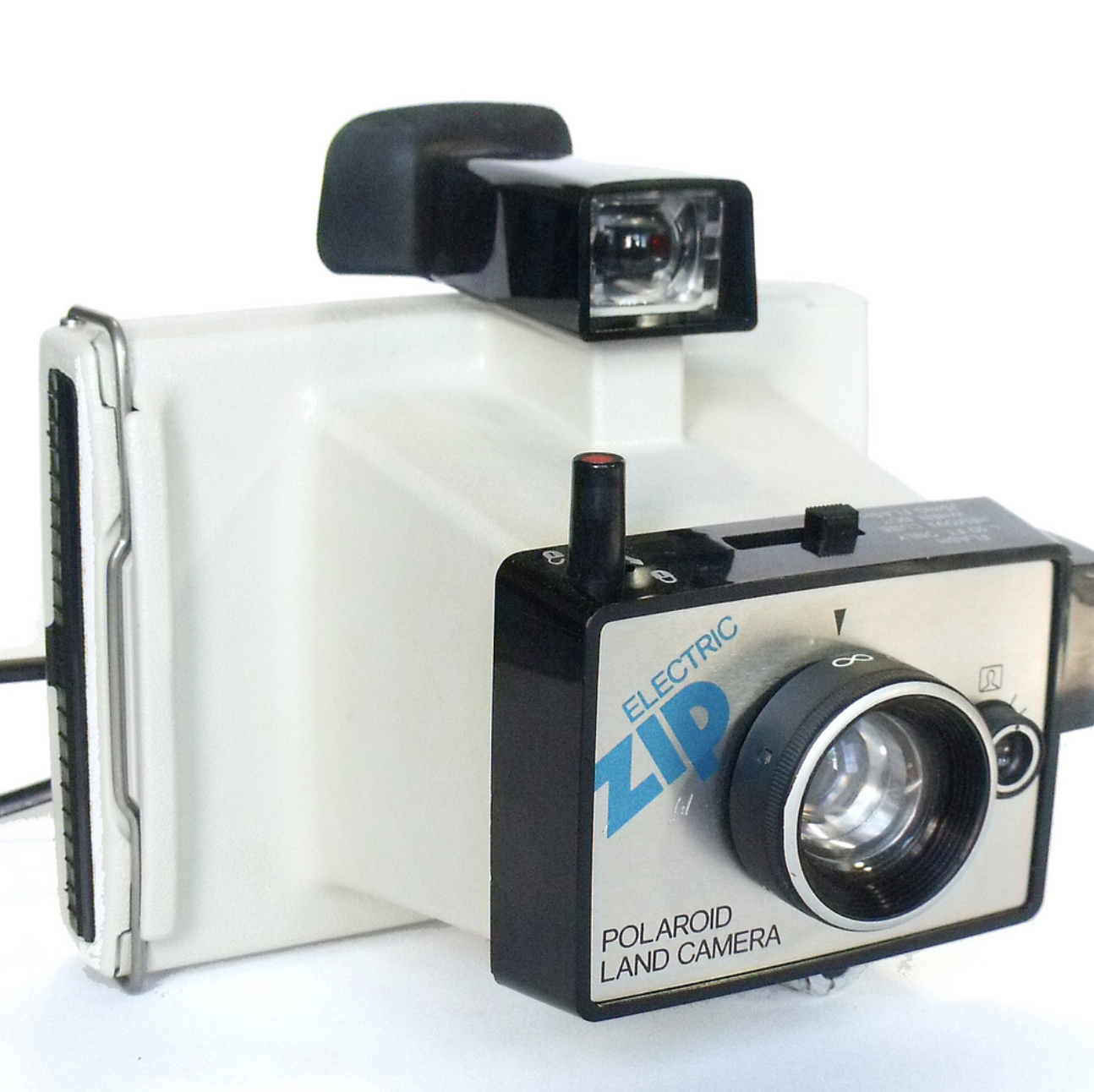

![]()
POLAROID ELECTRIC ZIP CAMERA- 1975-78. One of the less expensive Polaroids with an MSRP of $21.95 (about $89 in 2010 dollars). It was available in red, white, blue or black.
http://camerapedia.wikia.com/wiki/Polaroid_Electric_Zip
WHO INVENTED DIGITAL PHOTOGRAPHY? This question is often seen on web sites, but as shown by the material presented on this and previous pages, the correct answer is NO ONE. It has been a steady progression over time involving many persons, some who are noted on this and other sites, but much work has also been done by a multitude of anonymous engineers working for varius companies throughout the world. As noted below, Steve Sasson is given credit for construction of the first working, single unit digital camera that could be held in one's hands, but his work depended upon the efforts of many others. Some would like to arbitrarily give credit for the invention of digital photography to one person or another who envisioned such a device, but if that is to be the criteria, the credit for almost every known invention would have to go to various science fiction writers who "envisioned" such devices long before they were ever built. "Envisioning" such devices without detailed explanations of how they would actually be constructed, such as is required for patents, does not qualify in the minds of most as making one an inventor of such devices.


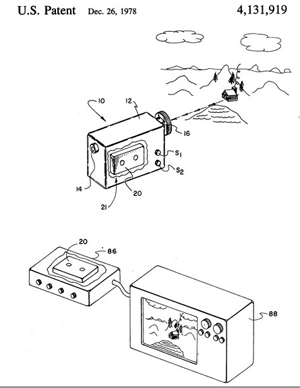


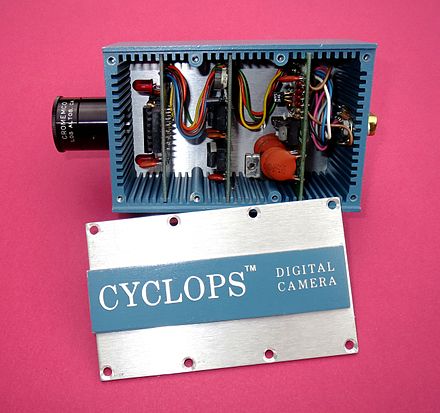
KODAK PROTOTYPE CCD DIGITAL CAMERA - 1975. A
Kodak engineer, Steve J. Sasson, holds a camera he constructed, the
world's first known CCD still image digital camera that was
self-contained - you could hold the entire camera in your hand - no
external devices such as computers were required (the Cromemco
Cyclops shown above was the first digital camera, but required use of a
computer such as the Altair - it was actually
marketed!) Sasson's camera used
the newly developed Fairchild black and white 100 X 100 Pixel (.01
megapixel) CCD as an image sensor and required 23 seconds to record a
single image onto digital cassette tape (photo shown on the right). The
camera weighed 8 1/2 pounds. Rochester (NY) Democrat &
Chronicle, page 8D, October 16, 2001.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steven_Sasson

![]()
HITACHI (SHIBA) SHIBADEN FP-100 - 1975. Example of a professional model closed circuit studio TV camera of the era. Lens:Shibaden Fujinon TV zoom 1:1.8, F=20-100mm. Shiba Electric merged with Hitachi Electric in 1973 to form Shinsei Hitachi Electronics.
http://www.labguysworld.com/Shiba-FP-100-Flyer.htm

![]()
MINOLTA SR-T 200 - 1975. Lens Minolta Rokkor f/2 50 mm. Shutter 1-1/1000 sec plus B. The above camera in near mint condition was obtained on eBay for $20 although Mckeown's indicates a price range of $100-$150.
http://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Minolta_SR-T_series

![]()
![]()
CANON 110ED, Vivitar 600 - 1975, 1976. The Canon 110ED and Vivitar 600 were two of many 110 cameras marketed by Canon, Vivitar and others during the 70's. Canon: lens f2/ 25mm. Shutter: 8 - 1/500sec. Vivitar: f8 24mm. Shutter 1/250 sec only.
www.mediajoy.com/ en/cla_came/canon110ed/
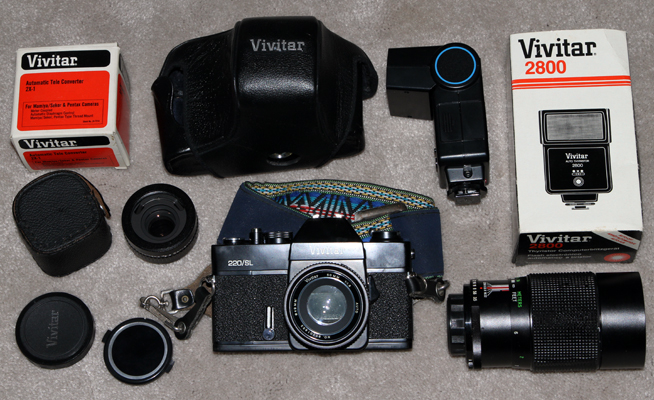

![]()
VIVITAR 220-SL - 1976. What will $25 get you these days? How about a Vivitar 220-SL 35 mm camera, a 50 mm lens, a 200 mm lens, a 2X tele adapter, and a flash, all in near mint condition. Unfortunately, the camera did not come with a manual. An original manual cost an additional $28.90, more than all the equipment previously mentioned!
http://www.flickr.com/groups/vivitaramniacs/


![]()
KEYSTONE XL200 - 1976-80. The XL200 had a fixed-focus f/1.1 lens with 9-18mm zoom. Exposure was by CdS photocell on Super 8 film. Original MSRP was around $122, which would be about $493 in 2012 dollars. All cameras have a story to tell, but unless you happen to know the previous owner you generally receive only the camera itself with no idea of its previous history. This case is a lttle different. The box contained the gift card shown above telling us a little bit about who it was purchased for and by whom. The outer envelope says mom and dad. The gift card tells us that this fairly expensive camera was intended to cover several occasions: Father's Day, Mother's Day, and someone's birthday; and was presumably given by their children, Nancy, Tim and Kim. If Nancy, Tim or Kim happens to come across this web site, be assured that your thoughtfull gift now has a happy home and will be well cared for indefinitely into the future.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keystone_Camera_Compan
KODAK ANALYST - 1975. If you like to collect unusual cameras there are many available, often quite inexpensively. For example, the Kodak Analyst Super 8 shown below is a Super 8 movie camera with one unusal feature - it has a timer which allows the user to take time lapse photographs rather than movies. The Analyst appears on eBay fairly frequently and can be purchased in excellent condition for about $30.


![]()
http://super8wiki.com/index.php/Kodak_Analyst
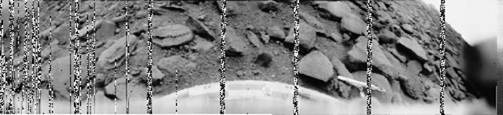

FIRST PHOTO FROM ANOTHER PLANET, VENERA-9 - 1975. On October 20, 1975 The Soviet lander Venera-9 transmitted the above panorama from Venus.
http://www.mentallandscape.com/C_CatalogVenus.htm
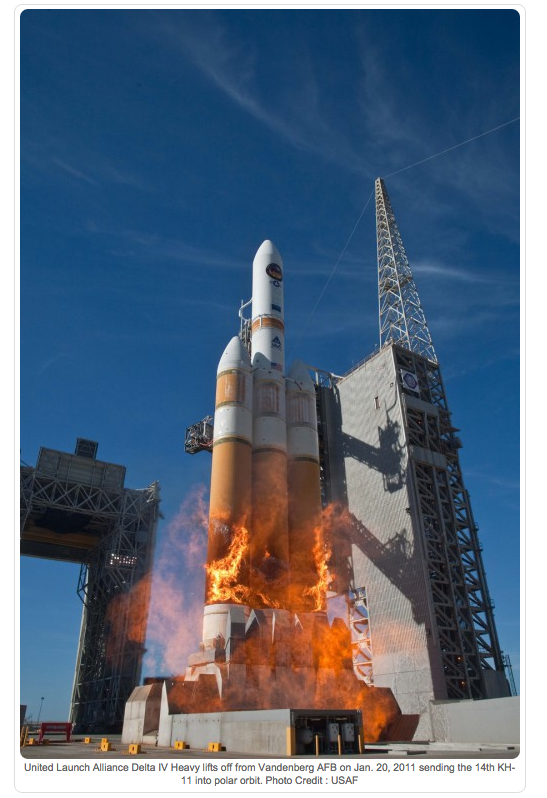



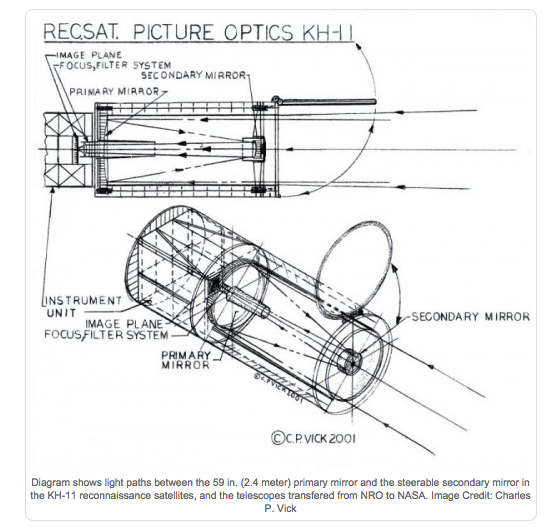


KH-11 RECONNAISSANCE SATELLITE - 1976.
The KH-11, referenced by the codenames Crystal and Kennan , also
commonly known as Big Bird, was a type of reconnaissance satellite
launched by the American National Reconnaissance Office from December
1976 to October 2005. Manufactured by Lockheed, the KH-11 was the first
American spy satellite to utilize electro-optical digital imaging, and
create a real-time optical observation capability. It is believed to
resemble the Hubble Space Telescope in size and shape, as the
satellites were shipped in similar containers. Using a powerful
2.3-meter mirror, the theoretical ground resolution with no atmospheric
degradation would be approximately 6 inches. Data was transmitted
through the United States military's Satellite Data System relay
network. Shown
above is a leaked KH-11 photo showing the Nikolaiev 444 shipyard in the
Black Sea taken in 1984. The KH-11 had a charge-coupled device
(CCD) array with a resolution of 800 x 800 pixels (0.64
megapixels). KH-11 satellites are believed to have been the source of
some imagery of the Soviet Union and China made public in
1997, as well as images of Sudan and Afghanistan made
public in 1998 that were related to the response to the 1998 U.S.
Embassy bombings.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/KH-11
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/KH-11_Kennan
http://photography2000.weebly.com/history.html
http://www.americaspace.com/?p=20825
CANON AE-1 - 1976.
First 35mm camera with built-in microprocessor (CPU - central processing unit). TTL Cds meter. About $630
with f1.4 lens. That would be about $2,549 in 2012 dollars. Click on image for enlarged view.
http://camerapedia.wikia.com/wiki/Canon_AE-1
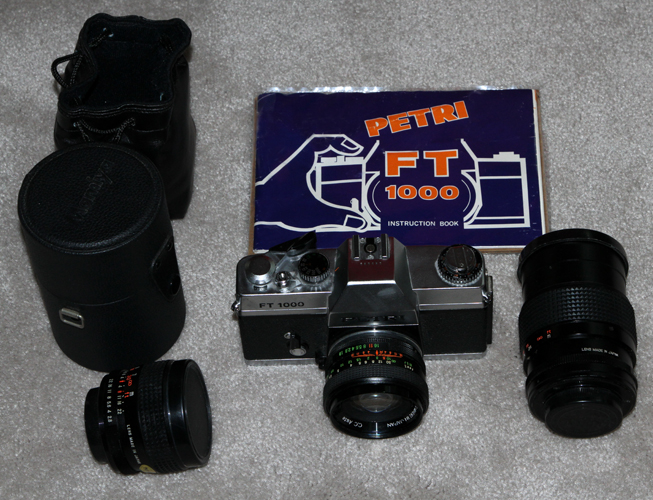

![]()
PETRI FT 1000 - 1976. Previously Kuribayashi, the Petri company went bankrupt in 1977. Those manufactured under the Kuribayashi name are quite rare and highly sought after in Japan. The above camera with three lenses, all in excellent condition, and an original manual were purchased on eBay for a winning bid of $10.
http://camerapedia.wikia.com/wiki/Petri
MINOLTA ZOOM SLR - 1976. First 110mm SLR camera. 25-50mm, f/4.5-f/16 zoom lens.
en.wikipedia.org/ wiki/Minolta_110_Zoom_SLR


![]()
5.25-INCH FLOPPY DISK - 1976. In 1976 Shugart Associates began production of 5.25 disk drives, believed to be the first standard computer medium that was not promulgated by IBM. On the right is something rarely seen these days outside of a museum - an unopened package of 5 1/4-inch floppies. Package kindly donated by our good friends, Ruth and Ken Schumacher.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floppy_disk
 VHS - 1976. JVC
introduced VHS (video home system),
the most successful of all home video formats. It was introduced as a
competitor of
Sony Betamax. 250 lines of resolution. Maximum
length of tape was 180 minutes in SP mode, 540 minutes in EP mode.
VHS - 1976. JVC
introduced VHS (video home system),
the most successful of all home video formats. It was introduced as a
competitor of
Sony Betamax. 250 lines of resolution. Maximum
length of tape was 180 minutes in SP mode, 540 minutes in EP mode.
http://www.labguysworld.com/formats.html
http://www.jvc.co.uk/template.php?page=100014
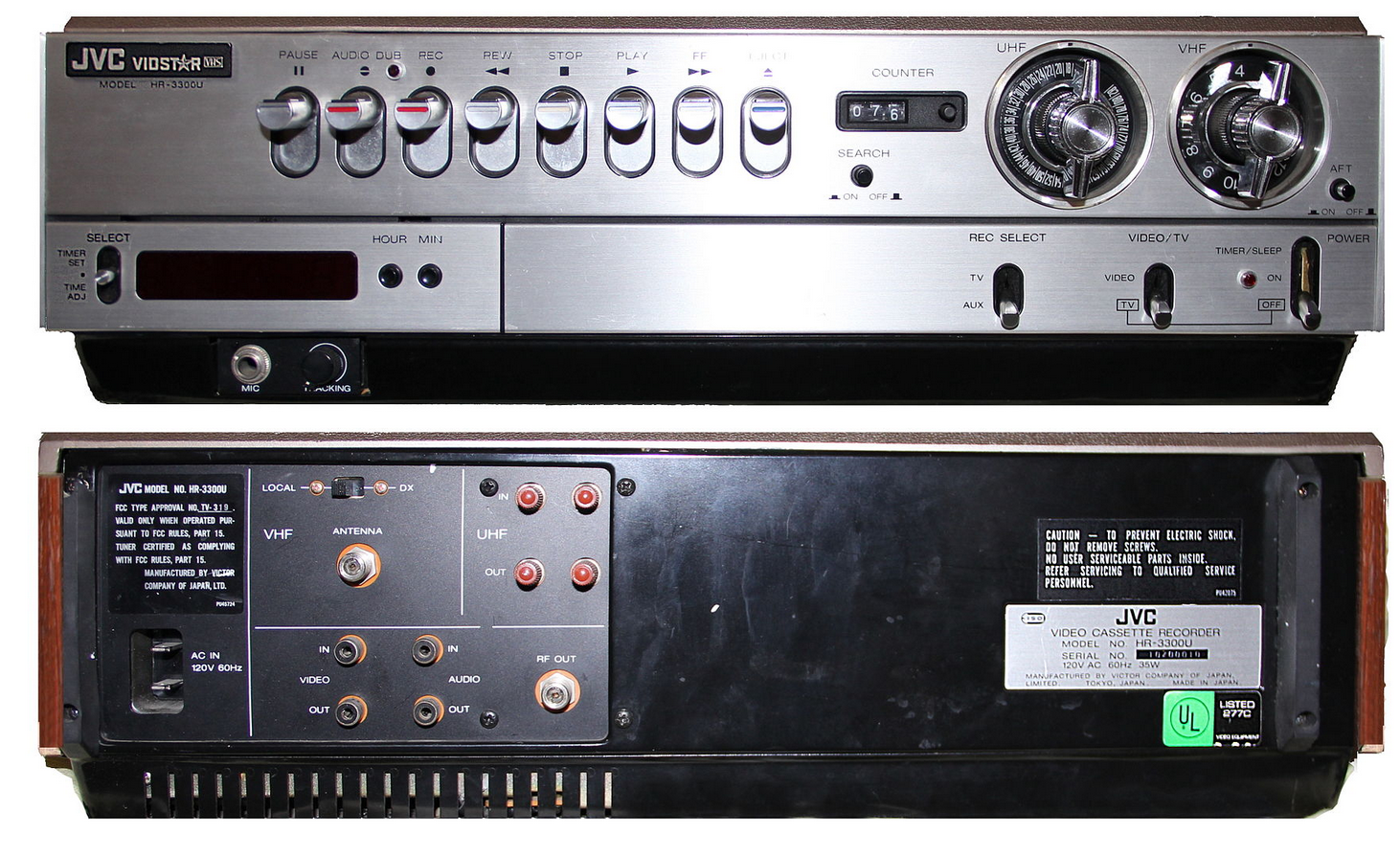


JVC HR-3300 - 1976. The
first VHS home video cassette recorder was introduced in Japan by Japan Victor
Corporation in September of 1976. In
April of 1976 JVC had demonstrated a VHS prototype to Sony, but Sony considered
VHS to be a copy of Beta and refused to adopt the VHS design. VHS
eventually replaced Sony's Betamax design in the comsumer market although
Beta is stilled used for non-consmer products.
http://www.rewindmuseum.com/vhs.htm


 SONY SL-7200
- 1976. The first stand-alone Sony Betamax
VCR in the United States, the SL-7200, came on the market in February 1976 priced
at $1295. This unit sold much better than the previous TV/VCR combo LV-1901.
The external clock to turn the unit on and off at preset times was an optional
accessory. The clock was placed externally at the request of Sony
chairman Akio Morita. Upon seeing a prototype unit in a lab with an internal
clock, he insisted that the clock be external so that if the clock malfunctioned
it could be repaired without requiring that the entire VCR be brought into a
service center. http://www.cedmagic.com/history/betamax-sl-7200-1976.html
SONY SL-7200
- 1976. The first stand-alone Sony Betamax
VCR in the United States, the SL-7200, came on the market in February 1976 priced
at $1295. This unit sold much better than the previous TV/VCR combo LV-1901.
The external clock to turn the unit on and off at preset times was an optional
accessory. The clock was placed externally at the request of Sony
chairman Akio Morita. Upon seeing a prototype unit in a lab with an internal
clock, he insisted that the clock be external so that if the clock malfunctioned
it could be repaired without requiring that the entire VCR be brought into a
service center. http://www.cedmagic.com/history/betamax-sl-7200-1976.html

 APPLE
I - 1977. Apple introduced its first home
computer, the Apple I. The Apple I was based on the MOStek 6502 chip,
whereas most other kit computers were built from the Intel 8080. The
Apple I was sold through several small retailers and included only the circuit
board. Users bought the workings and built their own case.
A tape-interface was sold separately. The Apple I's initial cost was $666.66.
Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, the most famous members of the Homebrew Computer
Club, designed the Apple I in 1976. Many leaders in mainline computer
companies like IBM and Digital did not believe that personal computers were
powerful enough to have a market. Sales of the Apple I and other PC's
that followed proved them wrong. Click on image to see enlarged view.
APPLE
I - 1977. Apple introduced its first home
computer, the Apple I. The Apple I was based on the MOStek 6502 chip,
whereas most other kit computers were built from the Intel 8080. The
Apple I was sold through several small retailers and included only the circuit
board. Users bought the workings and built their own case.
A tape-interface was sold separately. The Apple I's initial cost was $666.66.
Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, the most famous members of the Homebrew Computer
Club, designed the Apple I in 1976. Many leaders in mainline computer
companies like IBM and Digital did not believe that personal computers were
powerful enough to have a market. Sales of the Apple I and other PC's
that followed proved them wrong. Click on image to see enlarged view.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apple_I


APPLE II- 1977.
The first Apple II's were shipped in June 1977 and retailed for $1298
each. The Apple II was the first computer with a color display, and it
had the BASIC programming language built-in, so it was ready-to-run
right out of the box. The Apple II could be considered the first
user-friendly system.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apple_II



CASI PHOTO SYSTEM - 1977. The
CASI was intended to be used for the making of portraits, the first
commercial use of such a system. It required the use of a TV camera,
computer and printer. The company, Computer Amusement Systems Inc., is
still in business. June 1984 Popular Science, page 129. Photo and
information provided by Mike Mozart, JeepersMedia.
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/history
https://cool.culturalheritage.org/videopreservation/BHoIT.pdf
http://www.youtube.com/user/JeepersMedia
https://cool.culturalheritage.org/videopreservation/BHoIT.pdf


![]()
KONICA C35-AF - 1977. Konica introduced the C35-AF, the world's first compact point-and-shoot autofocus camera. It used two mirrors, one of which pivoted as the lens changed focus. Image contrast was greatest when the two images merged on the focusing sensor. At that time a solenoid stopped the moving lens at the appropriate focus distance. Hexanon 38mm f/2.8 lens. Shutter 1/6- - 1/250 second. Built-in flash and motor drive
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Konica_C35_AF

![]()
ROLLEI 35T - 1978. When the Rollei 35 was first introduced in
1966, it was the world's smallest mass produced full frame 35 mm camera. It could fit in a shirt pocket (H = 2.57inches, W = 4 inches, D = 1.5 inches).
High quality all metal construction and high quality optics led to its great success.
The lens collapsed and receded into the body. Front mounted f-stop and shutter
speed controls were
linked to a match
needle" metering system. In order to make use of all available space
the hot shoe flash mount was positioned
on the bottom of the camera. Other oddities included a left hand film advance
and a completely removable back for film loading. Various models have been produced
with the SE model being the most advanced. Originally made in Germany, some production
was done in Singapore.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rollei_35

![]()
RCA BW003 - 1978. An
example of an early consumer video camera. The B-003 was a 2/3 inch
vidicon camera that was intended to compliment early VHS machines and
allow the consumer to shoot home movies. The viewfinder is a simple
peep sight with a reticule marked for either a 25mm or a 12.5mm lens
for close-up and/or wide angle shooting. The microphone was built into
the front of the camera. Many such early video cameras are available to
the collector very inexpensively. The one shown above was purchased on
eBay in excellent condition with manual, converter and cables for $20. MSRP about $400 ($1,300 in 2015).
http://www.mediamaestro.net/audiovideo.htm

![]()
KODAK TELE-EKTRA - 1978. Kodak's version of an inexpensive 110 camera. Many manufacturers produced 110 cameras during this time period and they make an interesting collection in and of themselves. They take up very little space and most are very inexpensive. The above camera in excellent condition with manual and a box of vintage flashbulbs was purchased for $3.00.
http://camerapedia.wikia.com/wiki/Kodak_Tele_Ektra_32





![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Kodak Instant Cameras - 1976-86. In October 1985, after nine years
of patent litigation with Polaroid, Kodak was banned from making and selling instant
cameras and film. The ban took effect January 1986, at which time Kodak announced
a trade-in program. The owners of 16.5 million cameras were given the chance to
trade in their cameras for a share of Kodak common stock, a new camera, or $50
worth of Kodak merchandise. By June of 1986, several
class action lawsuits had been filed against Kodak by instant camera owners. The
final settlement called for owners to return the camera's nameplate for a refund
of cash and credits. The numerous Kodak Instant cameras
without nameplates have virtually no collector or commercial value. Some Kodak
instant cameras have the following names: Champ, Colorburst, EK, Handle, Happy Times,
Kodamatic, Partyflash, Party Star, Partytime, Pleaser, Trimprint. Shown
above left to right: Colorburst 100 (1978-80) MSRP $45, two Colorburst 200 (1978-80), MSRP $59.50, EK4 (1976-78), MSRP $53.50, The Handle
(1977-79), MSRP $39.95, and The Handle2 (1979-81), MSRP $40.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/instant_camera
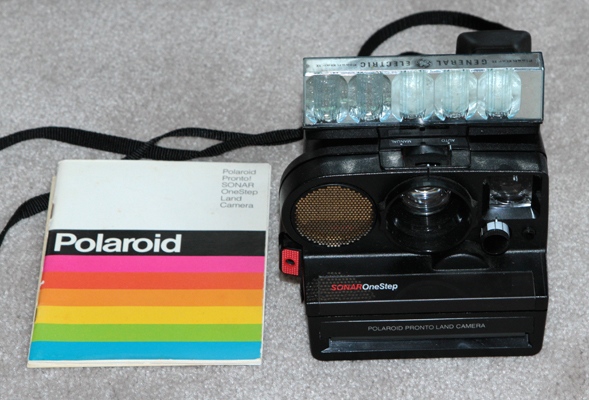

![]()
POLAROID SONAR ONESTEP PRONTO - 1978. The Sonar Onestep was one of the rather unique cameras that Polaroid produced using high frequency sound waves to operate the autofocus system. That is, it determined the distance to the subject in somewhat the same way as a bat does, by emitting high frequency sounds that bounces back to the camera, but which cannot be heard by human ears.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Polaroid_instant_cameras
NOVELTIES - One area where one can collect a great many photography items without spending a lot of money and without requiring a lot of storage space. The types of camera novelties available on eBay is almost unlimited: cuff links, cups, clothing, toys, office accessories, decorative items, fake cameras, storage containers, etc. Several are shown below.

![]()
COCA-COLA CHRISTMAS EDITION CAN CAMERA - 1970s. One of many can cameras made in the late 70s and early 80s. A 110 camera was fitted inside. Most can cameras were made by Eiko. With few exceptions, all of Eiko's cameras were "can cameras", that is, cameras built into a tin can. These were often sold or given away as promotions by soda and beer manufacturers. Various models were made from 1977 to 1983, but they all included a 110 camera hidden inside a can with a variety of nameplates. Many came from countries other than the U.S. and all were awkward to use.
https://www.darksilverblog.com/cancamera
https://www.flickr.com/photos/awcam/8711535128

![]()
FISHER PRICE GO TO THE ZOO CAMERA TOY - 1973. Each time the yellow button is pushed the flash cube rotates and a different zoo animal appears in the viewer.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CKij2HeEl7E

 MODERN VIDEO DISC / LASER DISC - 1978.
Philips and Sony collaborated to make digital imagery a reality (see
THE VIDEO DISK - 1961. David Paul Gregg). Sound and images
were digitally recorded and imprinted as micro-pits on a disc. A
laser then optically scanned the information and converted it into
pictures and sound on a home TV. Pioneer made use of the format
as Karaoke Entertainment which made the format popular in commercial
circles of Asia. Discs and players are readily available on eBay. Lewis M. Branscom, Confessions of a Technophile, 1995, page 130
MODERN VIDEO DISC / LASER DISC - 1978.
Philips and Sony collaborated to make digital imagery a reality (see
THE VIDEO DISK - 1961. David Paul Gregg). Sound and images
were digitally recorded and imprinted as micro-pits on a disc. A
laser then optically scanned the information and converted it into
pictures and sound on a home TV. Pioneer made use of the format
as Karaoke Entertainment which made the format popular in commercial
circles of Asia. Discs and players are readily available on eBay. Lewis M. Branscom, Confessions of a Technophile, 1995, page 130



FIRST OPTICAL DISC PLAYER- 1978.
MCA DiscoVision and Philips worked together to introduce the new
system, with MCA focusing on disc mastering and replication and Philips
manufacturing and distributing the playback system through its Magnavox
line of electronics. In december of 1978 MCA discs and Magnavox VH-8000
players went on sale in three Atlanta Georgia stores at $749 for the
player. The technology later resulted in today's CDs.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laserdisc
NATIONAL CR-1 - 1978.
It appears to be a typical 110 camera with a built-in flash, but
has something extra - an internal AM radio. It was
first marketed in 1978, and was followed by C-R2 and C-R3 models.
The C-R2 model was also sold as the Vivitar Radio 110 (see
elow). 24mm (f5.6), fixed-focus lens. Single speed shutter.
The
film is advanced by a lever on the bottom. The radio and flash are
powered by two AAA batteries. The camera can be used without the
batteries. Also marketed as the Radicame C-R1. MSRP 290
German Marks, about $580. The above sample was purchased on eBay in 2025 in excellent condition with flash and radio still working for $22.
https://www.radiomuseum.org/r/panasonic_flash_camera_with_radio_c_r1.html#google_vignette
http://www.subclub.org/shop/national.htm
http://www.subclub.org/shop/cr1.htm
http://www.submin.com/110/collection/national/index.htm
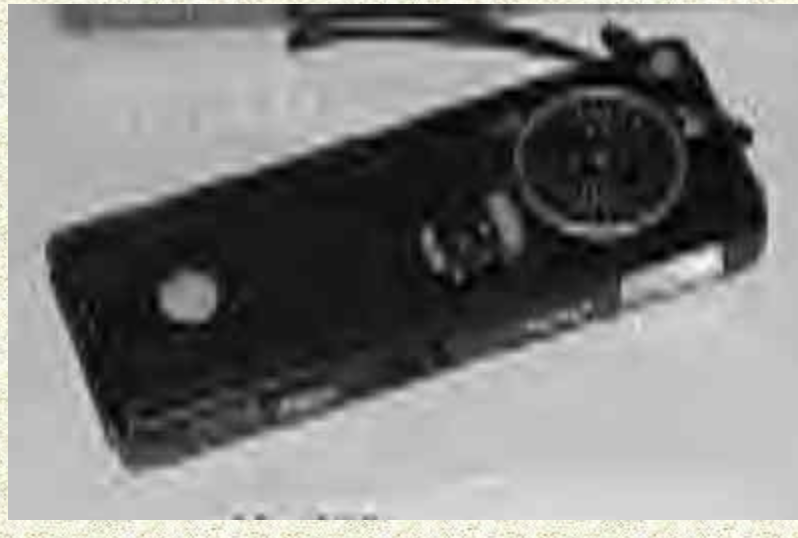


Vivitar Radio 110 - 1978.
Produced by Panasonic as were the National radio 110 cameras.
Same camera as the National C-R2. National C-R2 shown on the
right. An updated version of the C-R1 with a Fuji lens.
External changes from the C-R1 included the round speaker covering
instead of rectangular. In addition, the radio controls are
re-positioned, as is the three-way OFF/radio/camera switch.
Available in all black or with a colored face-plate. Marked with
the Panasonic symbol on the top. Also sold as the Vivitar Radio
110.
https://camera-wiki.org/wiki/Vivitar_Radio_110
https://www.radiomuseum.org/r/panasonic_camera_radio_c_r2.html#google_vignette




![]()
![]()
SONY HVC-1000 - 1979. The HVC-1000 is an example of an early Beta video camera. Originally, the HVC-1000 required an adapter to record to Beta recorders. Later, it could record directly to the Sony SL-2000 and SL-2500 of 1982. The Sony BC-300 battery charger shown on the right was for NP-11 batteries used in Betamovie camcorders. It's somewhat unique in that it held three batteries and charged them sequentially one at a time. User could select the order of charging. Once a battery was charged it could be removed while the remainder continued to charge. Sony information provided by Jack Carter, Sony technician. The above camera with fitted hard case was purchased in excellent condition for only $9.99. MSRP $1,329.
http://experimentaltvcenter.org/sony-hvc-1000-mf-trinicon-color-video-camera
https://playbackrental.wordpress.com/video-cameras/sony-hvc-1000-1979/
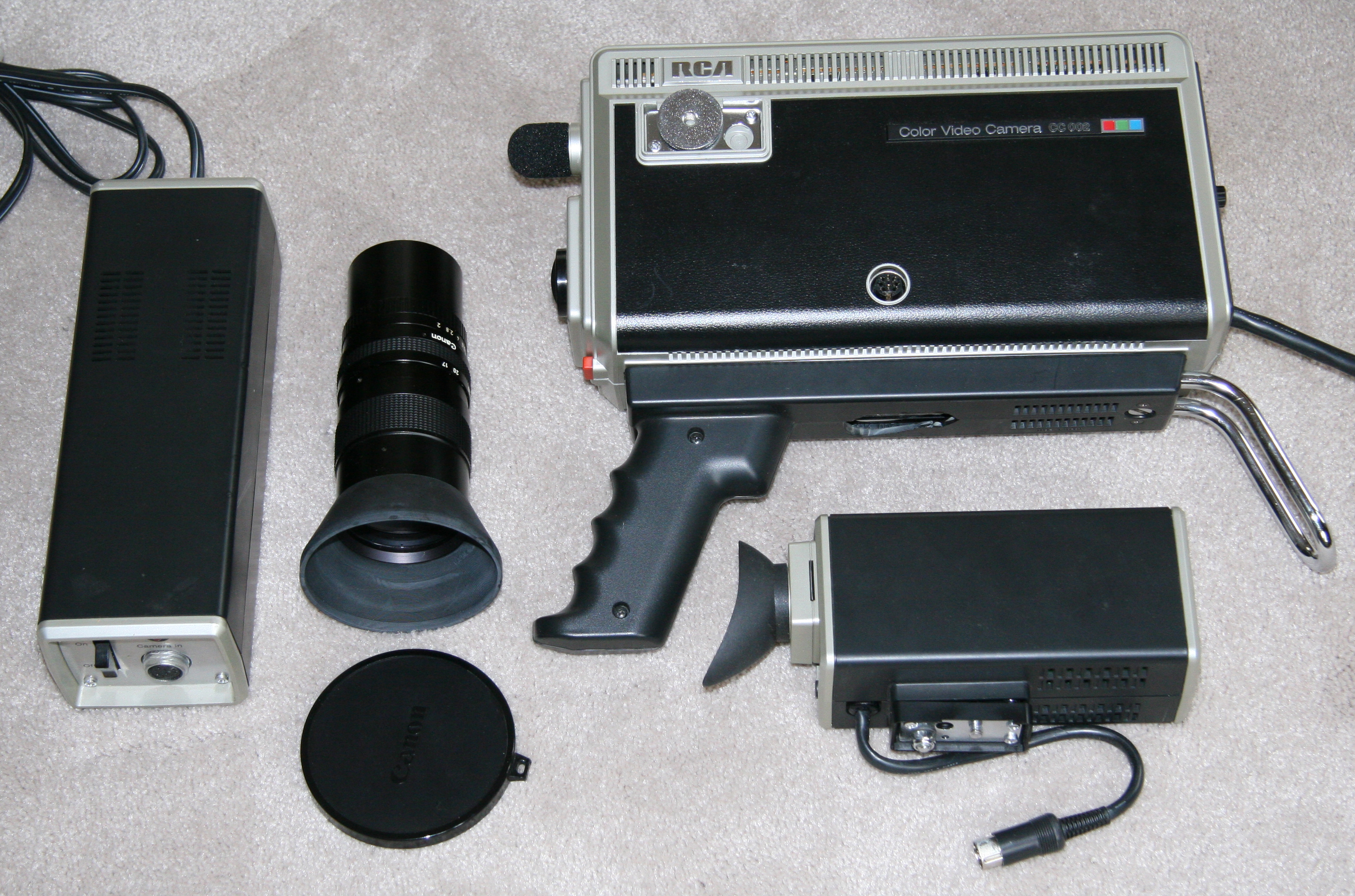

![]()
RCA CC002 - 1979. A
semi-professional closed circuit video camera of the type used by
various schools and universities. For those looking for a specialized
area of collecting these types of video cameras are often available on
eBay at a fraction of their original cost. The camera above in
excellent condition in its original box was obtained for only $44.
Although not apparent in the above photo, the CC002 is significanlty
bigger and heavier than the typical home video camera of the same era. MSRP $850, about $2,700 in 2015
http://www.labguysworld.com/Cat_RCA.htm

 DIGITAL AUDIO TAPE SYSTEM - 1979. Sony introduces digital
recording tape. CBS Records International is the
first major record company headquarted in the United States to take delivery
of Sony's new PCM-1600 (pulse code modulation) digital audio processor and editing
equipment.
DIGITAL AUDIO TAPE SYSTEM - 1979. Sony introduces digital
recording tape. CBS Records International is the
first major record company headquarted in the United States to take delivery
of Sony's new PCM-1600 (pulse code modulation) digital audio processor and editing
equipment.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_Audio_Tape

![]()
DURST M600 - 1979. Typical enlarger of the kind used during the era when many photography hobbyists developed and printed photos in their own home photo lab.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Durst


![]() SONY TPS-L2
WALKMAN - 1979. Sony introduced the Walkman TPS-L2 personal stereo.
A midnight-blue-and-silver with high quality sound, the TPS-L2 debuted
in July 1979. Called the Soundabout in the United States, it didn't record or
come with a speaker, but two could listen at once through a pair of headphone
jacks, and an orange button called the Hotline let the owner talk over the music.
MSRP $200.
SONY TPS-L2
WALKMAN - 1979. Sony introduced the Walkman TPS-L2 personal stereo.
A midnight-blue-and-silver with high quality sound, the TPS-L2 debuted
in July 1979. Called the Soundabout in the United States, it didn't record or
come with a speaker, but two could listen at once through a pair of headphone
jacks, and an orange button called the Hotline let the owner talk over the music.
MSRP $200.
 CCD CAMERAS
IN ASTRONOMY - 1979. An RCA 320 x 512-pixel
liquid nitrogen cooled CCD system began operation on a 1-meter telescope at
Kitt Peak National Observatory. Observations quickly demonstrated its
superiority over photographic plates. CCDs are best for high-resolution
imaging -- this is where they really come into their own. Because of the
dim light associated with large image scales, the relatively poor sensitivity
of photographic emulsions just cannot compete. CCD cameras are excellent
at imaging small planetary nebulae, and they can render thousands of obscure
galaxies as spectacular, exotic objects.
CCD CAMERAS
IN ASTRONOMY - 1979. An RCA 320 x 512-pixel
liquid nitrogen cooled CCD system began operation on a 1-meter telescope at
Kitt Peak National Observatory. Observations quickly demonstrated its
superiority over photographic plates. CCDs are best for high-resolution
imaging -- this is where they really come into their own. Because of the
dim light associated with large image scales, the relatively poor sensitivity
of photographic emulsions just cannot compete. CCD cameras are excellent
at imaging small planetary nebulae, and they can render thousands of obscure
galaxies as spectacular, exotic objects.



Kitt Peak National Observatory Orion Nebula (Click for large view.)
https://www.jstor.org/stable/40679073
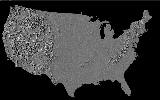
 RESPONSE
300 SYSTEM - 1979. Scitex, an Israel-based
company, marketed the Response 300 System which created full-color separations
and allowed the operator to change image details or combine images. The
Scitex Response 300 represented the first generally available technology that
allowed treatment of a graphic arts page as a data file that could be electronically
manipulated as a complete entity. Prior to that time, electronics and
computers had seen use in graphic arts, but only to process data on the fly,
without storage and without the ability to edit, change and manipulate complete
page images. The U.S. topographic map at left was created using the Scitex
Response 300 System. Click on image for enlarged view.
RESPONSE
300 SYSTEM - 1979. Scitex, an Israel-based
company, marketed the Response 300 System which created full-color separations
and allowed the operator to change image details or combine images. The
Scitex Response 300 represented the first generally available technology that
allowed treatment of a graphic arts page as a data file that could be electronically
manipulated as a complete entity. Prior to that time, electronics and
computers had seen use in graphic arts, but only to process data on the fly,
without storage and without the ability to edit, change and manipulate complete
page images. The U.S. topographic map at left was created using the Scitex
Response 300 System. Click on image for enlarged view.
http://www.referenceforbusiness.com/history2/99/Scitex-Corporation-Ltd.html
http://www.prepressure.com/prepress/history/events-1970-1979

![]()
NIKON EM - 1979. The EM was intended to compete in the price range of the Canon AE-1 and Olympus OM-10. The above camera in near mint condition with two lenses, a flash and a very nice camera bag was obtained on eBay for $36.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nikon_EM

ELIJAH EUGENE CAMPBELL - 1979. In 1979, Elijah Eugene Campbell of New Zealand designed an electronic still camera, but was unable to interest any of the major electronics manufactures. In 1981, Sony demonstrated the MAVICA still video camera which, in effect, obviated the need for Campbell to continue with his project.
https://www.digitalkameramuseum.de/en/history
https://prezi.com/nz_wji4ih5ky/the-evelution-of-camera/
1970s